Systematic review and narrative synthesis of the key barriers and facilitators to the delivery and uptake of primary healthcare services to women in Pakistan
- PMID: 37899162
- PMCID: PMC10619014
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076883
Systematic review and narrative synthesis of the key barriers and facilitators to the delivery and uptake of primary healthcare services to women in Pakistan
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of this review is to (1) identify barriers and facilitators with respect to women's health services at a primary care level based on a systematic review and narrative synthesis and (2) to conclude with recommendations for better services and uptake.
Design: Systematic review and narrative synthesis.
Data sources: PubMed, BMC Medicine, Medline, CINAHL and the Cochrane Library. Grey literature was also searched.
Eligibility criteria: Qualitative, quantitative and mixed studies were included in the review.
Data extraction and synthesis: The search took place at the beginning of June 2021 and was completed at the end of August 2021. Studies were included in the review based on the Sample, Phenomenon of Interest, Design, Evaluation, Research type criteria. The quality of the included studies was assessed using the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool. Data were synthesised using a narrative synthesis approach.
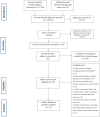
Results: A total of 33 studies were included in the review. We identified six barriers to the delivery of effective primary healthcare for women's health which have been organised under two core themes of 'service barriers' and 'family/cultural barriers'. Ten barriers to the uptake of primary healthcare for women have been identified, under three core themes of 'perceptions about healthcare service', 'cultural factors' and 'practical issues'. Three facilitators of primary healthcare delivery for women were identified: 'motivating community health workers (CHWs) with continued training, salary, and supervision' and 'selection of CHWs on the basis of certain characteristics'. Five facilitators of the uptake of primary healthcare services for women were identified, under two core themes of 'development of trust and acceptance' and 'use of technology'.
Conclusions: Change is needed not only to address the limitations of the primary healthcare services themselves, but also the cultural practices and limited awareness and literacy that prevent the uptake of healthcare services by women, in addition to the wider infrastructure in terms of the provision of financial support, public transport and child care centres.
Prospero registration number: CRD42020203472.
Keywords: health policy; primary health care; systematic review.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Population . Government of Pakistan, Pakistan economic survey 2022-23. n.d. Available: https://www.finance.gov.pk/survey/chapters_23/12_Population.pdf
-
- Chandrasiri J, et al. Impact of out-of-pocket expenditures on families and barriers to use of health services in Pakistan: evidence from the Pakistan social and living standards measurement surveys 2005-2007. Asian Development Bank 2012.
-
- Hanedar E, Walker S, Brollo F. n.d. Pakistan: spending needs for reaching sustainable development goals (sdgs). SSRN Journal 10.2139/ssrn.4026282 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources