PCMT1 regulates the migration, invasion, and apoptosis of prostate cancer through modulating the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway
- PMID: 37899170
- PMCID: PMC10637816
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205152
PCMT1 regulates the migration, invasion, and apoptosis of prostate cancer through modulating the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway
Abstract
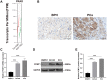
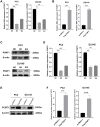
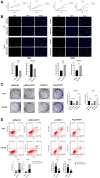
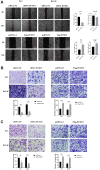
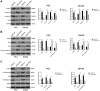
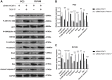
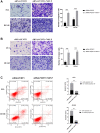
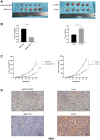
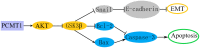
Protein L-isoaspartate (D-aspartate) O-methyltransferase (PCMT1) is a repair enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of isomerized aspartic acid (iso-Asp) residues into their normal structure, thereby restoring the configuration and function of proteins. Studies have shown that PCMT1 is overexpressed in several tumors and affects patients' prognosis. However, there are few reports on the role of PCMT1 in prostate cancer (PCa). In the present research, with the assistance of The Cancer Genome Atlas Program (TCGA) database, we found that PCMT1 was overexpressed in PCa tissues. The results of quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), western blot and immunohistochemistry staining also showed that PCMT1 expression was significantly increased in PCa tissues and cell lines. In PCa clinical samples, PCMT1 expression was closely related to Gleason score, clinical stage, lymph node metastasis and bone metastasis. The experiments of overexpression and knockdown of PCMT1 in vitro or in vivo showed that PCMT1 can significantly promote the proliferation, migration and invasion of PCa cells, inhibit cell apoptosis, and promote the growth of PCa. We furthermore confirmed that PCMT1 regulated the migration, invasion and apoptosis of PCa cells by modulating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT kinase/glycogen-synthase kinase-3β (PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β) signaling pathway. Collectively, PCMT1 plays a cancer-facilitative role in PCa by promoting the proliferation, migration and invasion of PCa cells, and inhibiting apoptosis. Therefore, PCMT1 is considered to represent a novel target for treating PCa.
Keywords: PCMT1; PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
PCMT1 is an unfavorable predictor and functions as an oncogene in bladder cancer.IUBMB Life. 2018 Apr;70(4):291-299. doi: 10.1002/iub.1717. Epub 2018 Mar 8. IUBMB Life. 2018. PMID: 29517839
-
Silencing PCMT1 enhances the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to paclitaxel through the PI3K/Akt/STMN1 pathway.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2024 Jun;103(6):e14559. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14559. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2024. PMID: 38853025
-
Activation of the PI3K/Akt signal transduction pathway and increased levels of insulin receptor in protein repair-deficient mice.Aging Cell. 2005 Feb;4(1):1-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9728.2004.00136.x. Aging Cell. 2005. PMID: 15659208
-
ST6Gal-I overexpression facilitates prostate cancer progression via the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 4;7(40):65374-65388. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11699. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27588482 Free PMC article.
-
The PI3K/AKT pathway in the pathogenesis of prostate cancer.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016 Jun 1;21(5):1084-91. doi: 10.2741/4443. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016. PMID: 27100493 Review.
Cited by
-
EPHB1 Protein Promoted the Progression of Prostate Adenocarcinoma Through Phosphorylating GSK3B and Activating EPHB1-GSK3B-SMAD3 Pathway.Hum Mutat. 2025 Jun 12;2025:4961883. doi: 10.1155/humu/4961883. eCollection 2025. Hum Mutat. 2025. PMID: 40548257 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics Analysis Sheds Light on the Extracellular Role of PCMT1.J Proteome Res. 2025 Jun 6;24(6):2832-2845. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c01111. Epub 2025 Apr 27. J Proteome Res. 2025. PMID: 40287848 Free PMC article.
-
Ginsenoside Re Regulates Oxidative Stress through the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Mice with Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairments.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Oct 13;46(10):11359-11374. doi: 10.3390/cimb46100677. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39451557 Free PMC article.
-
Important Roles of PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway and Relevant Inhibitors in Prostate Cancer Progression.Cancer Med. 2024 Nov;13(21):e70354. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70354. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39485722 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Heidenreich A, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Joniau S, Mason M, Matveev V, Mottet N, Schmid HP, van der Kwast T, Wiegel T, Zattoni F, and European Association of Urology. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and treatment of clinically localised disease. Eur Urol. 2011; 59:61–71. 10.1016/j.eururo.2010.10.039 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

