Smartphone Addiction Among University Students' During the Post-COVID-19 Era: The Role of Emotional Intelligence and Future Anxiety
- PMID: 37899219
- PMCID: PMC10620330
- DOI: 10.30773/pi.2023.0021
Smartphone Addiction Among University Students' During the Post-COVID-19 Era: The Role of Emotional Intelligence and Future Anxiety
Abstract
Objective: Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) pandemic-related psychological symptoms can lead to smartphone addiction (SPA) risk and other behavioral disorders, thus impacting individuals' mental health and well-being. The present study aims to propose a mediation model to investigate the association between emotional intelligence (EI) and SPA, and the mediating role of future anxiety (FA) during the post-COVID-19 era.
Methods: An online questionnaire including the Emotional Intelligence Scale, the Dark Future Scale, and the Smartphone Addiction Scale among university students from China, was conducted between September 14 and November 22, 2022. Finally, 1,154 valid questionnaires were collected. The reliability and confirmatory factor analysis results showed that all three scales had good reliability and validity.
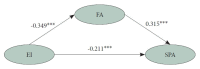
Results: Structural Equation Model demonstrated that EI significantly and negatively influenced SPA (β=0.211, p<0.001), university students' FA significantly and positively effected SPA (β=0.315, p<0.001), EI significantly predicted SPA in university students, and FA partially mediated the association between EI and SPA. The mediation effect of FA was 0.110, which accounted for 34.27% of the total effect. Bootstrap results furthermore tested the rigor of the mediating effect.
Conclusion: These findings broaden our understanding regarding the relationship between EI and SPA and the mediating role of FA, providing new sights for educators on how to reduce the risk of SPA when confronting the ongoing and possible future pandemics.
Keywords: Emotional intelligence; Future anxiety; Post-COVID-19 era; Smartphone addiction; University students.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COVID-19 victimization experience and university students' smartphone addiction: the mediating role of emotional intelligence.BMC Public Health. 2023 Jul 22;23(1):1410. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16355-7. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37481541 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the mediating role of emotional intelligence in the relationship between internet addiction and mental health among university students.PLOS Digit Health. 2024 Nov 20;3(11):e0000639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000639. eCollection 2024 Nov. PLOS Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 39565763 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19-Related Post-Traumatic Stress Disorders Relation With Social Media Addiction Among University Students: Mediating Role of Fear of Missing Out.Psychiatry Investig. 2024 Sep;21(9):994-1006. doi: 10.30773/pi.2024.0112. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Psychiatry Investig. 2024. PMID: 39155551 Free PMC article.
-
Smartphone addiction risk, technology-related behaviors and attitudes, and psychological well-being during the COVID-19 pandemic.Front Psychol. 2022 Aug 16;13:997253. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.997253. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36051208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Relationship Between Boredom and Smartphone Addiction Before and After the Outbreak of the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Psychol Rep. 2025 Jan 27:332941251314713. doi: 10.1177/00332941251314713. Online ahead of print. Psychol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39868931 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection of Depressive Symptoms in College Students Using Multimodal Passive Sensing Data and Light Gradient Boosting Machine: Longitudinal Pilot Study.JMIR Form Res. 2025 Jun 3;9:e67964. doi: 10.2196/67964. JMIR Form Res. 2025. PMID: 40460426 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of emotional intelligence on problematic mobile social media use: mediating role of peer relationships and experiential avoidance.Front Psychol. 2025 Jun 19;16:1558733. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1558733. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40612993 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional Intelligence and Behavioural Addictions: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 10;14(4):1125. doi: 10.3390/jcm14041125. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40004656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Elhai JD, Levine JC, Dvorak RD, Hall BJ. Non-social features of smartphone use are most related to depression, anxiety and problematic smartphone use. Comput Hum Behav. 2017;69:75–82.
-
- Abbasi GA, Jagaveeran M, Goh YN, Tariq B. The impact of type of content use on smartphone addiction and academic performance: physical activity as moderator. Technol Soc. 2021;64:101521.
-
- Lepp A, Barkley JE, Karpinski AC. The relationship between cell phone use, academic performance, anxiety, and satisfaction with life in college students. Comput Hum Behav. 2014;31:343–350.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources