Significance of the p38MAPK-CRP2 axis in myofibroblastic phenotypic transition
- PMID: 37899269
- PMCID: PMC11496777
- DOI: 10.1247/csf.23060
Significance of the p38MAPK-CRP2 axis in myofibroblastic phenotypic transition
Abstract
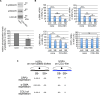
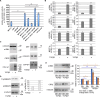
We have recently demonstrated that a LIM domain protein, cysteine and glycine-rich protein 2 (CSRP2 [CRP2]), plays a vital role in the functional expression of myofibroblasts and cancer-associated fibroblasts. CRP2 binds directly to myocardin-related transcription factors (MRTF [MRTF-A or MRTF-B]) and serum response factor (SRF) to stabilize the MRTF/SRF/CArG-box complex, leading to the expression of smooth muscle cell (SMC) genes such as α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and collagens. These are the marker genes for myofibroblasts. Here, we show that the adhesion of cultured human skin fibroblasts (HSFs) to collagen reduces the myofibroblastic features. HSF adhesion to collagen suppresses the expression of CRP2 and CSRP2-binding protein (CSRP2BP [CRP2BP]) and reduces the expression of SMC genes. Although CRP2BP is known as an epigenetic factor, we find that CRP2BP also acts as an adaptor protein to enhance the function of CRP2 mentioned above. This CRP2BP function does not depend on its histone acetyltransferase activity. We also addressed the molecular mechanism of the reduced myofibroblastic features of HSFs on collagen. HSF adhesion to collagen inhibits the p38MAPK-mediated pathway, and reducing the p38MAPK activity decreases the expression of CRP2 and SMC genes. Thus, the activation of p38MAPK is critical for the myofibroblastic features. We also show evidence that CRP2 plays a role in the myofibroblastic transition of retinal pigment epithelial cells (RPEs). Like HSFs, such phenotypic modulation of RPEs depends on the p38MAPK pathway.Key words: CRP2, p38MAPK, MRTF, myofibroblasts, retinal pigment epithelial cells.
Keywords: CRP2; MRTF; myofibroblasts; p38MAPK; retinal pigment epithelial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Role of CRP2-MRTF interaction in functions of myofibroblasts.Cell Struct Funct. 2023;48(1):83-98. doi: 10.1247/csf.23004. Cell Struct Funct. 2023. PMID: 37164693 Free PMC article.
-
CD44 inhibits α-SMA gene expression via a novel G-actin/MRTF-mediated pathway that intersects with TGFβR/p38MAPK signaling in murine skin fibroblasts.J Biol Chem. 2019 Aug 23;294(34):12779-12794. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007834. Epub 2019 Jul 8. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31285260 Free PMC article.
-
The benzoylphenylurea derivative BPU17 acts as an inhibitor of prohibitin and exhibits antifibrotic activity.Exp Cell Res. 2024 Sep 1;442(1):114221. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114221. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Exp Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 39182665
-
Myocardin-related transcription factor-A complexes activate type I collagen expression in lung fibroblasts.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 23;286(51):44116-44125. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.276931. Epub 2011 Nov 2. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22049076 Free PMC article.
-
The actin-MRTF-SRF gene regulatory axis and myofibroblast differentiation.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2012 Dec;5(6):794-804. doi: 10.1007/s12265-012-9397-0. Epub 2012 Aug 17. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2012. PMID: 22898751 Review.
References
-
- Gasparics, Á. and Sebe, A.. 2018. MRTFs- master regulators of EMT. Dev. Dyn., 247: 396–404. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

