Chinese medicine Jiangzhuo mixture regulates glucose and lipid metabolism in obese rats through TLR4/I κ B α/NF- κ B signaling pathway
- PMID: 37899401
- PMCID: PMC10630061
- DOI: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2023-0164
Chinese medicine Jiangzhuo mixture regulates glucose and lipid metabolism in obese rats through TLR4/I κ B α/NF- κ B signaling pathway
Abstract
Objectives: To explore the mechanism of Chinese medicine Jiangzhuo mixture regulating glucose and lipid metabolism in obese rats.
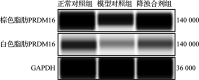
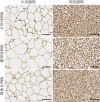
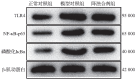
Methods: Thirty healthy male SD rats were randomly divided into normal control group, model control group, and Jiangzhuo mixture treatment group, with 10 rats in each group. The rats in the normal control group were fed with normal diet, the obesity model was induced by feeding high-fat diet in the model control group and the Jiangzhuo mixture treatment group, the rats in the treatment group were given with Jiangzhuo mixture 50 g/kg by gavage. After 8 weeks of intervention, the blood glucose (GLU), total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels were measured in the three groups. Quantitative reverse transcription PCR were used to detect the expression levels of PR domain containing 16 (PRDM16) and uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) in white and brown adipose tissues of the rats in each group; Western blotting was used to detect the expression of PRDM16 in the white and brown adipose tissue of rats, and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and inhibitor of NF-κB alpha (IκBα) in the white adipose tissue; immunohistochemistry was used to detect the expression of UCP1 protein in white and brown adipose tissues.
Results: Compared with the normal control group, the white fat weight (P<0.01), white fat coefficient (P<0.05) and Lee's coefficient (P<0.01) were significantly increased in the model control group; the contents of GLU, TC, TG and LDL-C were all increased, and the content of TG was significantly increased (P<0.05) in the model control group. The mRNA and protein expression levels of PRDM16 and UCP1 in white fat and brown fat were significantly decreased (P<0.05) in the model control group. Compared with the model control group, the white fat weight and white fat coefficient and Lee's coefficient were significantly reduced in the Jiangzhuo mixture treatment group (all P<0.01), the levels of GLU, TC, TG, and LDL-C in the the treatment group were all reduced, and the content of TG was reduced more obviously (P<0.01); expression levels of PRDM16 and UCP1 mRNA and protein were increased in brown and white adipose tissue. Compared with the normal control group, the expression levels of TLR4, phospho-IκBα and NF-κB-p65 proteins in white adipose tissue of the model control group were significantly increased (all P<0.01), while the expression levels of these proteins in the treatment group were significantly lower than those in the model control group (all P<0.05).
Conclusions: Jiangzhuo mixture can alleviate high-fat diet-induced increase in body fat, abnormal expression of biochemical indexes and promote the expression of key proteins including UCP1 and PRDM16 in white and brown adipose tissues by regulating TLR4/IκBα/NF-κB signaling pathway.
目的: 探究降浊合剂影响肥胖大鼠糖脂代谢的机制。方法: 30只健康雄性SD大鼠随机分为正常对照组、模型对照组、降浊合剂组,每组各10只,其中正常对照组给予普通饲料喂养,模型对照组给予高脂饲料喂养,降浊合剂组在给予高脂饲料喂养的同时给予50 g/kg降浊合剂浓缩液灌胃。各组干预8周后,采用全自动生化分析仪检测各组大鼠血糖、总胆固醇、三酰甘油、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)和高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)水平;采用定量逆转录PCR法检测各组大鼠白色、棕色脂肪中PR结构域蛋白16(PRDM16)、解偶联蛋白1(UCP1)信使RNA表达;采用蛋白质印迹法检测各组大鼠白色、棕色脂肪中PRDM16以及各组大鼠白色脂肪中Toll样受体4(TLR4)、磷酸化核因子抑制蛋白(IκBα)和核因子κB(NF-κB)蛋白表达水平;采用免疫组织化学法检测各组大鼠白色、棕色脂肪中UCP1蛋白表达水平。结果: 与正常对照组比较,模型对照组白色脂肪质量(P<0.01)、白色脂肪系数(P<0.05)和Lee’s系数(P<0.01)均显著升高;血糖、总胆固醇、三酰甘油、LDL-C含量均升高,其中三酰甘油含量升高明显(P<0.05);白色脂肪和棕色脂肪PRDM16、UCP1的信使RNA和蛋白表达水平均明显降低(均P<0.05)。与模型对照组比较,降浊合剂组的白色脂肪质量、白色脂肪系数和Lee’s系数均明显降低(均P<0.01);血糖、总胆固醇、三酰甘油、LDL-C含量均有所降低,其中三酰甘油含量明显降低(P<0.01);棕色脂肪和白色脂肪中PRDM16、UCP1的信使RNA和蛋白的表达水平上升。此外,与正常对照组比较,模型对照组白色脂肪中TLR4、磷酸化IκBα和NF-κB-p65蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.01),而降浊合剂组上述蛋白的表达水平相对于模型对照组显著下降(均P<0.05)。结论: 降浊合剂可以通过调节SD大鼠体内TLR4/IκBα/NF-κB信号通路缓解高脂饮食诱导的体脂增加、生化指标异常表达及促进关键转录因子UCP1和PRDM16在白色、棕色脂肪中的表达,进而抑制肥胖大鼠的体脂形成,降低体重,缓解肥胖。.
Keywords: Jiangzhuo mixture; Lipid metabolism; Obese; PR domain containing 16; SD rats; Saccharometabolism; Uncoupling protein 1.
Conflict of interest statement
所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Electroacupuncture intervention improves lipid metabolism and promotes browning of white adipose tissue by activating AMPK/Sirt1 pathway and up-regulating Nrg4 content in middle-aged and aged obese rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023 Aug 25;48(8):764-72. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20230187. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023. PMID: 37614134 Chinese.
-
[Electroacupuncture activates PKA / CREB signaling pathway to promote browning of white fat in obese rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025 May 25;50(5):553-566. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20240755. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40390613 Chinese.
-
[Electroacupuncture intervention promotes browning of white adipose tissue by regulating LKB1/AMPK pathway in obese mice].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025 Apr 25;50(4):393-401. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20240109. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40262937 Chinese.
-
[Effect of electroacupuncture stimulation of different acupoint groups on lipid metabolism and liver TLR4/NF-κB signaling in obese rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021 Oct 25;46(10):845-50. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20210522. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021. PMID: 34698458 Chinese.
-
Meta-analysis and machine learning reveal the antiobesity effects of melatonin on obese rodents.Obes Rev. 2024 May;25(5):e13701. doi: 10.1111/obr.13701. Epub 2024 Feb 4. Obes Rev. 2024. PMID: 38311366 Review.
Cited by
-
Ethyl acetate extract of Knoxia roxburghii (Rubiaceae) down-regulates ECHDC1, CAMK2D, DDB1, UBA6, BIRC6, and HK1 proteins and ameliorates the symptoms of diabetes mellitus.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 22;16:1587858. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1587858. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40766763 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 刘阳, 张赛, 董高芳, 等. 高强度间歇训练通过支配内脏脂肪的交感神经活动促进白色脂肪组织棕色化[J]. 中国体育科技, 2020, 56(2): 15-23. 10.16470/j.csst.2019226 - DOI
- LIU Yang, ZHANG Sai, DONG Gaofang, et al. . High-intensity interval training promotes white adipose tissue browning through sympathetic activity that innervates visceral fat[J]. China Sport Science and Technology, 2020, 56(2): 15-23. (in Chinese) 10.16470/j.csst.2019226. 10.16470/j.csst.2019226 - DOI - DOI
-
- 董笑克, 刘铜华, 常青, 等. 辣木叶醇提物对自发型肥胖型糖尿病大鼠非酒精性脂肪性肝病的影响[J]. 环球中医药, 2019, 12(8): 1149-1153. 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1749.2019.08.003 - DOI
- DONG Xiaoke, LIU Tonghua, CHANG Qing, et al. . Effects of ethanol Moringa Oleifera leaves extract on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in ZDF rats[J]. Global Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 12(8): 1149-1153. (in Chinese) 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1749.2019.08.003. 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1749.2019.08.003 - DOI - DOI
-
- 喻松仁, 白洋, 王河宝, 等. 温胆汤对肥胖大鼠血清瘦素及下丘脑STAT3和SOCS3表达的影响[J]. 中医杂志, 2019, 60(3): 57-61.
- YU Songren, BAI Yang, WANG Hebao, et al. . Effect of Wendan Decoction on serum leptin and expression of STAT3 and SOCS3 in hypothalamus of obese rat[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 60(3): 57-61. (in Chinese)
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous