Rifaximin Alfa and Liver Diseases: More Than a Treatment for Encephalopathy, a Disease Modifier
- PMID: 37899985
- PMCID: PMC10612522
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S425292
Rifaximin Alfa and Liver Diseases: More Than a Treatment for Encephalopathy, a Disease Modifier
Abstract
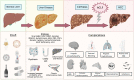
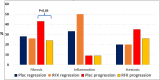
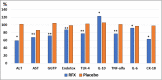
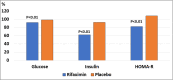
RFX, a rifamycin-based antibacterial agent obtained by the culture of the actinomycete Streptomyces mediterranei, has a broad antibacterial spectrum covering gram- positive, gram-negative, aerobic, and anaerobic bacteria. RFX is an antibiotic that elicits its effect by inhibiting bacterial RNA synthesis. When administered orally, its intestinal absorption is extremely low (<0.4%), restricting antibacterial activity mainly in the intestinal tract, with few systemic side effects. RFX has been recommended by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver guidelines for the treatment of HE. RFX may contribute to restore hepatic function and to decrease the development of liver fibrosis. Its efficacy has been shown in patients with previous hepatic encephalopathy and several complications, such as infections, including spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, ascites and oesophageal variceal bleeding. Thus, RFX has an outstanding role in the therapeutic arsenal in hepatic cirrhosis, under the concept of disease modifier.
Keywords: hepatic cirrhosis therapy; liver disease; modifier; rifaximin.
© 2023 Torre et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AT and JCG have no conflicts of interests related to this publication. ACFM is medical advisor of Alfasigma Laboratories Mexico.
Figures


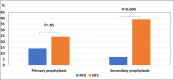
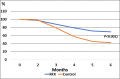
References
-
- Younunossi ZH, Stepanova M, Younossi Y, et al. Epidemiology of chronic liver Diseases in USA in the past three decades. Gut. 2020;69:203–209. - PubMed
-
- Escorcia Charriz EJ, et al. INEGI Comunicado de prensa núm 592/21. Bioc. 2018;13:17–30.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

