HOXC Cluster Antisense RNA 3, a Novel Long Non-Coding RNA as an Oncological Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Human Malignancies
- PMID: 37899986
- PMCID: PMC10612484
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S425523
HOXC Cluster Antisense RNA 3, a Novel Long Non-Coding RNA as an Oncological Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Human Malignancies
Abstract
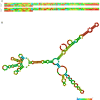
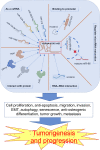
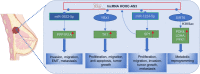
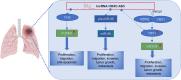
HOXC cluster antisense RNA 3 (HOXC-AS3) is a novel long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) that exhibits aberrant expression patterns in various cancer types. Its expression is closely related to clinicopathological features, demonstrating significant clinical relevance across multiple tumors. And HOXC-AS3 plays multifaceted roles in tumor progression, impacting cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), autophagy, senescence, tumor growth, and metastasis. In this review, we summarized and comprehensively analyzed the expression and clinical significance of HOXC-AS3 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for malignancies. Additionally, we presented an in-depth update on HOXC-AS3's functions and regulatory mechanisms in cancer pathogenesis. This narrative review underscores the importance of HOXC-AS3 as a promising lncRNA candidate in cancer research and its potential as a predictive biomarker and therapeutic target in clinical applications.
Keywords: HOXC-AS3; biological marker; long non-coding RNA; malignant neoplasms; neoplastic processes.
© 2023 Xie et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LncRNA HOXC-AS3 overexpression inhibits TGF-β2-induced colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion by sponging miR-1269.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022 Jan-Dec;41:9603271221093630. doi: 10.1177/09603271221093630. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35537198
-
LncRNA HOXC-AS3 accelerates malignant proliferation of cervical cancer cells via stabilizing KDM5B.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Jun 6;150(6):294. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05799-y. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38842683 Free PMC article.
-
The Long Non-Coding RNA HOXC-AS3 Promotes Glioma Progression by Sponging miR-216 to Regulate F11R Expression.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 23;12:845009. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.845009. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35402226 Free PMC article.
-
A concise review of the regulatory, diagnostic, and prognostic implications of HOXB-AS3 in tumors.J Cancer. 2024 Jan 1;15(3):714-728. doi: 10.7150/jca.91033. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38213732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The integrated comprehension of lncRNA HOXA-AS3 implication on human diseases.Clin Transl Oncol. 2022 Dec;24(12):2342-2350. doi: 10.1007/s12094-022-02920-w. Epub 2022 Aug 20. Clin Transl Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35986859 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long Noncoding RNA VLDLR-AS1 Levels in Serum Correlate with Combat-Related Chronic Mild Traumatic Brain Injury and Depression Symptoms in US Veterans.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 25;25(3):1473. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031473. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338752 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

