Investigating salivary concentration of calcium ion in hypothyroidism
- PMID: 37900090
- PMCID: PMC10600405
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.1669
Investigating salivary concentration of calcium ion in hypothyroidism
Abstract
Background and aims: Hypothyroidism is the most common disease of the thyroid gland. Thyroid hormone plays a crucial role in regulating tissue growth and metabolism. Additionally, patients with thyroid dysfunction have a higher incidence of caries and periodontal problems. The presence of calcium and phosphate ions seems to be effective in remineralizing teeth and reducing caries. The aim of this study was to evaluate the salivary level of calcium in patients with hypothyroidism.
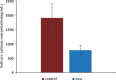
Results: The results of this study showed that saliva calcium concentration in patients with hypothyroidism is significantly lower than healthy subjects. Also, no significant association was found between salivary calcium levels and TSH and T4 hormones level of blood.
Conclusion: The increased prevalence of dental caries in patients with hypothyroidism may be related to a decrease in their calcium levels.
Keywords: calcium; hypothyroidism; salivary.
© 2023 The Authors. Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- NS VB, Patel PB. Oral health status of children suffering from thyroid disorders. J Indian Soc Pedodont Preventive Dentistr. 2020;34(2):139‐144. - PubMed
-
- Ayala C, Lemus O, Frías M. Oral and systemic manifestations of congenital hypothyroidism in children. A case report. J Oral Res. 2015;4(5):329‐334.
-
- Talebi S, Ghaedi E, Sadeghi E, et al. Trace element status and hypothyroidism: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020;197(1):1‐14. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources