Associated Biochemical and Hematological Markers in COVID-19 Severity Prediction
- PMID: 37900669
- PMCID: PMC10602699
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/6216528
Associated Biochemical and Hematological Markers in COVID-19 Severity Prediction
Abstract
Background: The global threat of COVID-19 has created the need for researchers to investigate the disease's progression, especially through the use of biomarkers to inform interventions. This study aims to assess the correlations of laboratory parameters to determine the severity of COVID-19 infection.
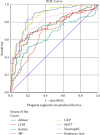
Methods: This study was conducted among 191 COVID-19 patients in Sumeru Hospital, Lalitpur, Nepal. According to their clinical outcomes, these patients were divided into severe and nonsevere groups. Inflammatory markers such as LDH, D-dimer, CRP, ferritin, complete blood cell count, liver function tests, and renal function tests were performed. Binary logistic regression analysis determined relative risk factors associated with severe COVID-19. The area under the curve (AUC) was calculated with ROC curves to assess the potential predictive value of risk factors.
Results: Out of 191 patients, 38 (19.8%) subjects died due to COVID-19 complications, while 156 (81.7%) survived and were discharged from hospital. The COVID-19 severity was found in patients with older age and comorbidities such as CKD, HTN, DM, COPD, and pneumonia. Parameters such as d-dimer, CRP, LDH, SGPT, neutrophil, lymphocyte count, and LMR were significant independent risk factors for the severity of the disease. The AUC was highest for d-dimer (AUC = 0.874) with a sensitivity of 82.2% and specificity of 81.2%. Similarly, the cut-off values for other factors were age >54.5 years, D-dimer >0.91 ng/ml, CRP >82.4 mg/dl, neutrophil >78.5%, LDH >600 U/L, and SGPT >35.5 U/L, respectively.
Conclusion: Endorsement of biochemical and hematological parameters with their cut-off values also aids in predicting COVID-19 severity. The biomarkers such as D-dimer, CRP levels, LDH, ALT, and neutrophil count could be used to predict disease severity. So, timely analysis of these markers might allow early prediction of disease progression.
Copyright © 2023 Anit Lamichhane et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Poor Prognostic Biochemical Markers Predicting Fatalities Caused by COVID-19: A Retrospective Observational Study From a Developing Country.Cureus. 2020 Aug 5;12(8):e9575. doi: 10.7759/cureus.9575. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32913691 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality in Patients of COVID-19 Infection: Biochemical Markers and its Cut-off Values for Predicting Outcome.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2022 Jan;32(1):37-41. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2022.01.37. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2022. PMID: 34983145
-
Can Hematological Ratios Predict Outcome of COVID-19 Patients? A Multicentric Study.J Blood Med. 2021 Jun 29;12:505-515. doi: 10.2147/JBM.S316681. eCollection 2021. J Blood Med. 2021. PMID: 34234607 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory and hematologic markers as predictors of severe outcomes in COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Am J Emerg Med. 2021 Mar;41:110-119. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.12.076. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Am J Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 33418211 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and COVID-19: The Impact of Hematological Biomarkers on Disease Severity and Outcomes.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 17;14(8):2765. doi: 10.3390/jcm14082765. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40283596 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Nomogram for Predicting Survival in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Pneumonia Based on Admission Data.Infect Drug Resist. 2025 Apr 25;18:2093-2104. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S509178. eCollection 2025. Infect Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40303607 Free PMC article.
-
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Modulates the Inflammatory Milieu and Organ Failure Trajectory in Severe COVID-19 and Sepsis.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 13;14(12):4224. doi: 10.3390/jcm14124224. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40565970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buchmueller T., Groening I., Ihl R. Predicting severity of Covid-19 using standard laboratory parameters. medRxiv . 2021
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous