Impact of Intrahepatic External Beam Radiotherapy in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
- PMID: 37901765
- PMCID: PMC10601851
- DOI: 10.1159/000529635
Impact of Intrahepatic External Beam Radiotherapy in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
Introduction: We aimed to investigate whether concurrent use of intrahepatic external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) is a viable option for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) undergoing tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy.
Methods: A total of 453 patients with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage C (BCLC C) HCC, who started first-line treatment with TKI with intrahepatic EBRT (TKI + RT, n = 97) or TKI without intrahepatic EBRT (TKI, n = 356) were analyzed. The overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were compared in the overall cohort, patients who received at least 8 weeks of TKI treatment and a propensity score-matched cohort.
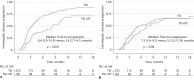
Results: OS and PFS were better in those treated with TKI + RT than TKI (8.6 vs. 4.4 months and 4.5 vs. 2.3 months, respectively, with p < 0.001). Of note, the TKI + RT group demonstrated significantly longer time to intrahepatic tumor progression. In subgroup analysis, TKI + RT led to better OS than TKI in all subgroups and PFS was significantly improved in patients without extrahepatic metastasis and those with portal vein invasion. There was no significant difference in treatment discontinuation due to adverse events between the TKI + RT and TKI groups (32.0% vs. 37.9%, p = 0.34). Furthermore, patients treated with TKI + RT showed better liver function preservation over time compared to TKI without intrahepatic EBRT. Comparable treatment outcomes were observed between patients who received at least 8 weeks of TKI treatment and the propensity score-matched cohort.
Conclusion: Concurrent intrahepatic EBRT targeting the liver and/or macrovascular invasion can be a viable option to improve outcomes of BCLC stage C patients receiving TKI therapy with an aim to control intrahepatic progression and preserving the liver function.
Keywords: Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage C; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Radiation therapy; Tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Concurrent nivolumab and external beam radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with macrovascular invasion: A phase II study.JHEP Rep. 2023 Dec 21;6(4):100991. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100991. eCollection 2024 Apr. JHEP Rep. 2023. PMID: 38463541 Free PMC article.
-
Strategy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma based on liver function and portal vein tumor thrombosis.Hepatol Res. 2020 Dec;50(12):1375-1385. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13567. Epub 2020 Sep 26. Hepatol Res. 2020. PMID: 32924266
-
Overall survival and toxicity of Y90 radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma patients in Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage C (BCLC-C).BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Nov 17;22(1):467. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02528-y. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36396989 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Therapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Update of a Rapidly Evolving Field.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019 Sep-Oct;9(5):588-596. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2019.07.012. Epub 2019 Aug 2. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31695249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of external-beam radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: An overview of current evidence according to the different target population.Biosci Trends. 2019 Mar 14;13(1):10-22. doi: 10.5582/bst.2018.01261. Epub 2019 Feb 24. Biosci Trends. 2019. PMID: 30799321 Review.
Cited by
-
CD276 enhances sunitinib resistance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma by promoting DNA damage repair and activation of FAK-MAPK signaling pathway.BMC Cancer. 2024 May 27;24(1):650. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12402-7. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38802739 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources