Association between pathologic response and survival after neoadjuvant therapy in lung cancer
- PMID: 37903504
- PMCID: PMC10803255
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-023-02660-6
Association between pathologic response and survival after neoadjuvant therapy in lung cancer
Abstract
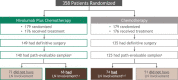
Neoadjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy improves event-free survival (EFS) and pathologic complete response (0% residual viable tumor (RVT) in primary tumor (PT) and lymph nodes (LNs)), and is approved for treatment of resectable lung cancer. Pathologic response assessment after neoadjuvant therapy is the potential analog to radiographic response for advanced disease. However, %RVT thresholds beyond pathologic complete response and major pathologic response (≤10% RVT) have not been explored. Pathologic response was prospectively assessed in the randomized, phase 3 CheckMate 816 trial (NCT02998528), which evaluated neoadjuvant nivolumab (anti-programmed death protein 1) plus chemotherapy in patients with resectable lung cancer. RVT, regression and necrosis were quantified (0-100%) in PT and LNs using a pan-tumor scoring system and tested for association with EFS in a prespecified exploratory analysis. Regardless of LN involvement, EFS improved with 0% versus >0% RVT-PT (hazard ratio = 0.18). RVT-PT predicted EFS for nivolumab plus chemotherapy (area under the curve = 0.74); 2-year EFS rates were 90%, 60%, 57% and 39% for patients with 0-5%, >5-30%, >30-80% and >80% RVT, respectively. Each 1% RVT associated with a 0.017 hazard ratio increase for EFS. Combining pathologic response from PT and LNs helped differentiate outcomes. When compared with radiographic response and circulating tumor DNA clearance, %RVT best approximated EFS. These findings support pathologic response as an emerging survival surrogate. Further assessment of the full spectrum of %RVT in lung cancer and other tumor types is warranted. ClinicalTrials.gov registration: NCT02998528 .
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.S.D. reports being named on a patent for system and method for annotating pathology images to predict patient outcome (US Provisional Patent Application: 63/313,548; filed 2/24/2022). A.C.-M. reports receiving grants or contracts from Bristol Myers Squibb. M.P. reports receiving grants or contracts from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Pfizer, Roche and Takeda; and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD, Pfizer, Roche and Takeda. P.M.F. reports research funding received by his institution from AstraZeneca, BioNTech, Bristol Myers Squibb, Corvus, Kyowa, Novartis and Regeneron; trial steering committee membership for AstraZeneca, BioNTech, Bristol Myers Squibb and Corvus; participation in advisory boards and reimbursement from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi, F-Star Therapeutics, G1 Therapeutics, Genentech, ITeos Therapeutics, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Sanofi and Surface; and leadership positions at Mesothelioma Applied Research Foundation and LUNGevity Foundation. J. Spicer reports research funding received by his institution from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, CLS Therapeutics, Protalix Biotherapeutics, Merck and Roche; receiving support for the present manuscript from Bristol Myers Squibb; consulting fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, Novartis, Protalix Biotherapeutics, Regeneron, Roche and Xenetic Biosciences; honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb and PeerView; participation on data safety monitoring/advisory boards for the PUCC trial; and leadership positions at the Canadian Association of Thoracic Surgeons (unpaid). N.G. reports receiving consulting fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi and Takeda; and meeting/travel support from Roche. R.A.A. reports receiving support for the present manuscript from Bristol Myers Squibb; grants or contracts from RAPT Therapeutics; consulting fees from AstraZeneca and MSD; and meeting/travel support from Bristol Myers Squibb. E.G. reports research funding received by his institution from the National Cancer Institute and Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs—Department of Defense; honoraria from the LUNGevity Foundation; expert testimony provided to Covington and Burling; and holding mutual funds and exchange traded funds. P.I. reports receiving support for the present manuscript from Bristol Myers Squibb; grants or contracts from Bristol Myers Squibb; consulting fees from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Merus, Roche and Sanofi; honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly and Genentech; and being a shareholder of Bristol Myers Squibb. J. Sunshine reports grants or contracts from Palleon Pharmaceuticals. K.M.K. reports consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Takeda and Ventana; and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Medscape, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, Prime Oncology, Roche and Ventana. M.T. is an employee and shareholder of Bristol Myers Squibb. J.B. is an employee and shareholder of Bristol Myers Squibb. J.C. is an employee and shareholder of Bristol Myers Squibb. V.D. is an employee and shareholder of Bristol Myers Squibb. J.N. is an employee and shareholder of Bristol Myers Squibb. D.B. is an employee and shareholder of Bristol Myers Squibb; and reports being named on a patent of Bristol Myers Squibb. T.R.C. reports research funding received by her institution from Janssen; and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer and TotalCME. J.M.T. reports receiving support for the present manuscript from Bristol Myers Squibb; consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck and Roche; participation on advisory boards from AstraZeneca; and being named on a patent for a machine learning algorithm for irPRC. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures














References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

