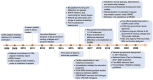
Health System Strengthening Through Professional Midwives in Bangladesh: Best Practices, Challenges, and Successes
- PMID: 37903587
- PMCID: PMC10615233
- DOI: 10.9745/GHSP-D-23-00081
Health System Strengthening Through Professional Midwives in Bangladesh: Best Practices, Challenges, and Successes
Abstract
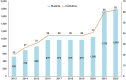
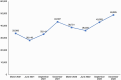
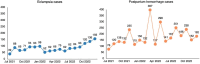
In 2008, a cadre of professional midwives was introduced in Bangladesh. Since then, 120 midwifery educational programs have been established. There are 2,556 midwives serving at 667 government health facilities, and there are more midwives working in nongovernmental organizations and the private sector. This case study documents the process of establishing a midwifery profession with distinct midwifery expertise in Bangladesh and aims to guide other low- and middle-income countries in best practices and challenges. We describe the national administrative groundwork for the profession's launch, roll-out of an education program aligned with the International Confederation of Midwives, national deployment, enabling environments in deployment, and the professional association. Bangladesh's professional midwives' roles in humanitarian response and the COVID-19 pandemic are also discussed. The first and final authors were closely involved in supporting the government's establishment of the profession, and their direct experience is drawn upon to contextualize the topics. In addition, the authors conducted a desk review of documents that supported the profession's integration into the health system and documented its results. Both routine program data and existing research studies were reviewed. Outcomes show that midwives are deployed to 95% of government subdistrict hospitals. About 50% of these hospitals are fully staffed with 4 midwives, and within the hospitals, midwives are in charge of 90% of the maternity wards and attend 75%-85% of the births. Since the midwives' deployment, significant quality improvement for most World Health Organization indicators has been found, along with increases in service utilization. The experience of establishing a new midwifery profession in Bangladesh shows that it is possible for a lower middle-income country to introduce a globally standard midwifery profession, distinct from nursing, to improve quality sexual, reproductive, maternal, newborn, and adolescent health services in both humanitarian and development settings.
© Begum et al.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Midwife-led pandemic telemedicine services for maternal health and gender-based violence screening in Bangladesh: an implementation research case study.Reprod Health. 2023 Aug 29;20(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s12978-023-01674-0. Reprod Health. 2023. PMID: 37644451 Free PMC article.
-
Implementing midwifery services in public tertiary medical college hospitals in Bangladesh: A longitudinal study.Women Birth. 2023 May;36(3):299-304. doi: 10.1016/j.wombi.2022.09.006. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Women Birth. 2023. PMID: 36154792
-
Effect on mortality of community-based maternity-care programme in rural Bangladesh.Lancet. 1991 Nov 9;338(8776):1183-6. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92041-y. Lancet. 1991. PMID: 1682600 Clinical Trial.
-
Strengthening quality in sexual, reproductive, maternal, and newborn health systems in low- and middle-income countries through midwives and facility mentoring: an integrative review.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023 Oct 5;23(1):712. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-06027-0. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023. PMID: 37798690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The state of professionalisation of midwifery in Belgium: A discussion paper.Women Birth. 2021 Feb;34(1):7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.wombi.2020.09.012. Epub 2020 Sep 26. Women Birth. 2021. PMID: 32988768 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring care quality in midwifery clinical practice settings in Ghana - a qualitative study.BMC Med Educ. 2025 Feb 20;25(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-06861-0. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 39980026 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of involvement of midwives in maternal care on patient and provider satisfaction in secondary-level public health facilities in Bangladesh: a comparative quasi-experimental study.J Glob Health. 2025 Jul 4;15:04183. doi: 10.7189/jogh.15.04183. J Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 40611805 Free PMC article.
-
Individual- and system-level determinants of breastfeeding in a low-resource setting.Front Public Health. 2024 Nov 6;12:1471252. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1471252. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39568606 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sustainable Development Goal 3: ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Accessed September 21, 2023. https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal3
-
- United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA). Comprehensive Midwifery Programme Guidance. UNFPA; 2014. Accessed September 21, 2023. https://www.unfpa.org/resources/midwifery-programme-guidance
-
- International Confederation of Midwives (ICM). International Definition of the Midwife. ICM; 2017. Accessed September 21, 2023. https://www.internationalmidwives.org/assets/files/definitions-files/201...
-
- International Confederation of Midwives (ICM). Essential Competencies for Midwifery Practice, 2019 Update. ICM; 2019. Accessed September 21, 2023. https://www.internationalmidwives.org/assets/files/general-files/2019/10...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
