PDK4-dependent hypercatabolism and lactate production of senescent cells promotes cancer malignancy
- PMID: 37903887
- PMCID: PMC10663165
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-023-00912-w
PDK4-dependent hypercatabolism and lactate production of senescent cells promotes cancer malignancy
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: PDK4-dependent hypercatabolism and lactate production of senescent cells promotes cancer malignancy.Nat Metab. 2024 May;6(5):980. doi: 10.1038/s42255-024-01054-3. Nat Metab. 2024. PMID: 38693321 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Author Correction: PDK4-dependent hypercatabolism and lactate production of senescent cells promotes cancer malignancy.Nat Metab. 2024 Jul;6(7):1416. doi: 10.1038/s42255-024-01069-w. Nat Metab. 2024. PMID: 38831001 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
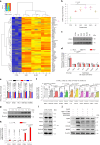
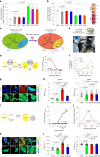
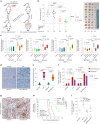
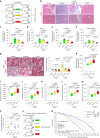
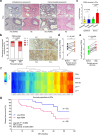
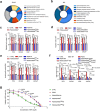
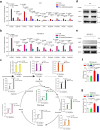
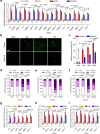
Senescent cells remain metabolically active, but their metabolic landscape and resulting implications remain underexplored. Here, we report upregulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4) upon senescence, particularly in some stromal cell lines. Senescent cells display a PDK4-dependent increase in aerobic glycolysis and enhanced lactate production but maintain mitochondrial respiration and redox activity, thus adopting a special form of metabolic reprogramming. Medium from PDK4+ stromal cells promotes the malignancy of recipient cancer cells in vitro, whereas inhibition of PDK4 causes tumor regression in vivo. We find that lactate promotes reactive oxygen species production via NOX1 to drive the senescence-associated secretory phenotype, whereas PDK4 suppression reduces DNA damage severity and restrains the senescence-associated secretory phenotype. In preclinical trials, PDK4 inhibition alleviates physical dysfunction and prevents age-associated frailty. Together, our study confirms the hypercatabolic nature of senescent cells and reveals a metabolic link between cellular senescence, lactate production, and possibly, age-related pathologies, including but not limited to cancer.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

