Imetelstat-mediated alterations in fatty acid metabolism to induce ferroptosis as a therapeutic strategy for acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 37904045
- PMCID: PMC10824665
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-023-00653-5
Imetelstat-mediated alterations in fatty acid metabolism to induce ferroptosis as a therapeutic strategy for acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
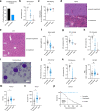
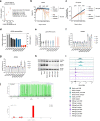
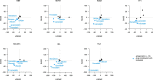
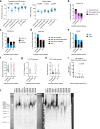
Telomerase enables replicative immortality in most cancers including acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Imetelstat is a first-in-class telomerase inhibitor with clinical efficacy in myelofibrosis and myelodysplastic syndromes. Here, we develop an AML patient-derived xenograft resource and perform integrated genomics, transcriptomics and lipidomics analyses combined with functional genetics to identify key mediators of imetelstat efficacy. In a randomized phase II-like preclinical trial in patient-derived xenografts, imetelstat effectively diminishes AML burden and preferentially targets subgroups containing mutant NRAS and oxidative stress-associated gene expression signatures. Unbiased, genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 editing identifies ferroptosis regulators as key mediators of imetelstat efficacy. Imetelstat promotes the formation of polyunsaturated fatty acid-containing phospholipids, causing excessive levels of lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress. Pharmacological inhibition of ferroptosis diminishes imetelstat efficacy. We leverage these mechanistic insights to develop an optimized therapeutic strategy using oxidative stress-inducing chemotherapy to sensitize patient samples to imetelstat causing substantial disease control in AML.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.W.L. has received research funding from Janssen related to imetelstat (2016–2018). For research beyond this study, S.W.L. has received funding from Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb (2019–2022), consultancy from Abbvie (2021–2023) and advisory board fees from Abbvie and Astellas (2020–2021). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures














References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

