ATP1A1/BCL2L1 predicts the response of myelomonocytic and monocytic acute myeloid leukemia to cardiac glycosides
- PMID: 37904054
- PMCID: PMC10776384
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-023-02076-8
ATP1A1/BCL2L1 predicts the response of myelomonocytic and monocytic acute myeloid leukemia to cardiac glycosides
Abstract
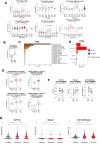
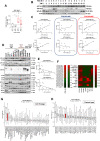
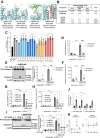
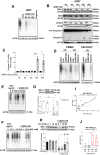
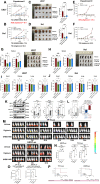
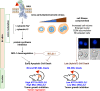
Myelomonocytic and monocytic acute myeloid leukemia (AML) subtypes are intrinsically resistant to venetoclax-based regimens. Identifying targetable vulnerabilities would limit resistance and relapse. We previously documented the synergism of venetoclax and cardiac glycoside (CG) combination in AML. Despite preclinical evidence, the repurposing of cardiac glycosides (CGs) in cancer therapy remained unsuccessful due to a lack of predictive biomarkers. We report that the ex vivo response of AML patient blasts and the in vitro sensitivity of established cell lines to the hemi-synthetic CG UNBS1450 correlates with the ATPase Na+/K+ transporting subunit alpha 1 (ATP1A1)/BCL2 like 1 (BCL2L1) expression ratio. Publicly available AML datasets identify myelomonocytic/monocytic differentiation as the most robust prognostic feature, along with core-binding factor subunit beta (CBFB), lysine methyltransferase 2A (KMT2A) rearrangements, and missense Fms-related receptor tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) mutations. Mechanistically, BCL2L1 protects from cell death commitment induced by the CG-mediated stepwise triggering of ionic perturbation, protein synthesis inhibition, and MCL1 downregulation. In vivo, CGs showed an overall tolerable profile while impacting tumor growth with an effect ranging from tumor growth inhibition to regression. These findings suggest a predictive marker for CG repurposing in specific AML subtypes.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NOXA-mediated degradation of MCL1 and BCL2L1 causes apoptosis of daunorubicin-treated human acute myeloid leukemia cells.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Nov;236(11):7356-7375. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30407. Epub 2021 May 13. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33982799
-
Inhibition of Bcl-2 Synergistically Enhances the Antileukemic Activity of Midostaurin and Gilteritinib in Preclinical Models of FLT3-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Nov 15;25(22):6815-6826. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0832. Epub 2019 Jul 18. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31320594 Free PMC article.
-
Erythroid/megakaryocytic differentiation confers BCL-XL dependency and venetoclax resistance in acute myeloid leukemia.Blood. 2023 Mar 30;141(13):1610-1625. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021011094. Blood. 2023. PMID: 36508699 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis targeted therapies in acute myeloid leukemia: an update.Expert Rev Hematol. 2020 Dec;13(12):1373-1386. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2020.1852923. Epub 2020 Dec 6. Expert Rev Hematol. 2020. PMID: 33205684 Review.
-
Targeted therapies in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: a focus on FLT-3 inhibitors and ABT199.Expert Rev Hematol. 2017 Oct;10(10):863-874. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2017.1366852. Epub 2017 Aug 21. Expert Rev Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28799432 Review.
Cited by
-
Tetrahydrobenzimidazole TMQ0153 targets OPA1 and restores drug sensitivity in AML via ROS-induced mitochondrial metabolic reprogramming.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Apr 7;44(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03372-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40197337 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

