Mechanisms of genotoxicity and proteotoxicity induced by the metalloids arsenic and antimony
- PMID: 37904059
- PMCID: PMC10616229
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-023-04992-5
Mechanisms of genotoxicity and proteotoxicity induced by the metalloids arsenic and antimony
Abstract
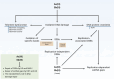
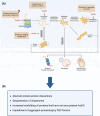
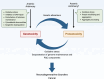
Arsenic and antimony are metalloids with profound effects on biological systems and human health. Both elements are toxic to cells and organisms, and exposure is associated with several pathological conditions including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. At the same time, arsenic- and antimony-containing compounds are used in the treatment of multiple diseases. Although these metalloids can both cause and cure disease, their modes of molecular action are incompletely understood. The past decades have seen major advances in our understanding of arsenic and antimony toxicity, emphasizing genotoxicity and proteotoxicity as key contributors to pathogenesis. In this review, we highlight mechanisms by which arsenic and antimony cause toxicity, focusing on their genotoxic and proteotoxic effects. The mechanisms used by cells to maintain proteostasis during metalloid exposure are also described. Furthermore, we address how metalloid-induced proteotoxicity may promote neurodegenerative disease and how genotoxicity and proteotoxicity may be interrelated and together contribute to proteinopathies. A deeper understanding of cellular toxicity and response mechanisms and their links to pathogenesis may promote the development of strategies for both disease prevention and treatment.
Keywords: Antimony toxicity; Arsenic toxicity; Genotoxicity; Metalloid; Protein aggregation; Protein folding; Proteostasis; Proteotoxicity.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanism of metalloid-induced death in Leishmania spp.: role of iron, reactive oxygen species, Ca2+, and glutathione.Free Radic Biol Med. 2006 May 15;40(10):1857-68. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.01.024. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006. PMID: 16678023
-
Emerging Trends in Metalloid-Dependent Signaling in Plants.Trends Plant Sci. 2021 May;26(5):452-471. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2020.11.003. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Trends Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33257259 Review.
-
Involvement of nitric oxide (NO) in plant responses to metalloids.J Hazard Mater. 2021 Oct 15;420:126606. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126606. Epub 2021 Jul 7. J Hazard Mater. 2021. PMID: 34271449 Review.
-
Mechanisms involved in metalloid transport and tolerance acquisition.Curr Genet. 2001 Aug;40(1):2-12. doi: 10.1007/s002940100234. Curr Genet. 2001. PMID: 11570513 Review.
-
Comparative and environmental genotoxicity of antimony and arsenic.Anticancer Res. 1997 Jul-Aug;17(4A):2603-7. Anticancer Res. 1997. PMID: 9252688
Cited by
-
Multilevel Regulation of Membrane Proteins in Response to Metal and Metalloid Stress: A Lesson from Yeast.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 18;25(8):4450. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084450. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38674035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct binding of arsenicals to nuclear transport factors disrupts nucleocytoplasmic transport.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 21:2025.01.13.632748. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.13.632748. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Cell Sci. 2025 Aug 15;138(16):jcs263889. doi: 10.1242/jcs.263889. PMID: 39868121 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes for Toxins Sensing in Environmental Samples-A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Apr 7;25(7):2339. doi: 10.3390/s25072339. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PRDX1 protects ATM from arsenite-induced proteotoxicity and maintains its stability during DNA damage signaling.Oncotarget. 2025 May 19;16:362-378. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28720. Oncotarget. 2025. PMID: 40387816 Free PMC article.
-
Lifetime water arsenic, genetic susceptibility, and bladder cancer in the New England Bladder Cancer Study.JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2025 Jul 1;9(4):pkaf064. doi: 10.1093/jncics/pkaf064. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40570095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shaji E, Santosh M, Sarath KV, Prakash P, Deepchand V, Divya BV. Arsenic contamination of groundwater: a global synopsis with focus on the Indian Peninsula. Geosci Front. 2021;12:101079. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.08.015. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

