Clinical efficacy of plasma exchange in systemic lupus erythematosus during pregnancy
- PMID: 37904711
- PMCID: PMC10566447
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.1041
Clinical efficacy of plasma exchange in systemic lupus erythematosus during pregnancy
Abstract
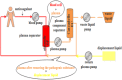
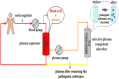
Objective: To investigate the clinical efficacy of plasma exchange (PE) with or without prednisone and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) during pregnancy.
Methods: The clinical characteristics of 14 pregnant women with SLE admitted to our hospital were retrospectively analyzed, including 7 only treated with prednisone and HCQ (non-PE group) as well as 7 combined PE (PE group). The delivery situations of 14 patients were recorded. Data like erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), urine protein, platelet count, and SLEDAI scores were compared between two groups before treatment and 3, 6, and 12 months after delivery.
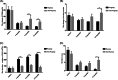
Results: Three patients in the non-PE group ended in miscarriage while all patients in the PE group were delivered successfully. Eleven successfully delivered fetuses in the two groups were healthy, and the Apgar scores were over 8. The ESR of the PE group was significantly lower than that of the non-PE group at 6 and 12 months after delivery, while there was no statistical difference in ESR between the two groups before treatment and 3 months after delivery. The ESR and urine protein were significantly higher in the non-PE group at months 3, 6, and 12 postpartum. There was a significant decrease in disease activity postpartum in the PE group compared to predelivery disease activity. The change in platelet counts between the two groups significantly increased over time in the PE group, while SLEDAI scores decreased.
Conclusions: The combination of PE and oral prednisone and HCQ is possibly a more effective treatment than oral prednisone and HCQ alone for patients with active SLE during pregnancy. This treatment option reduces pregnancy loss and promotes the patients' postpartum condition to a certain extent.
Keywords: efficacy; plasmapheresis; pregnancy; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2023 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical impact of hydroxychloroquine dose adjustment according to the American Academy of Ophthalmology guidelines in systemic lupus erythematosus.Lupus Sci Med. 2020 May;7(1):e000395. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2020-000395. Lupus Sci Med. 2020. PMID: 32434863 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of hydroxychloroquine on preterm delivery and intrauterine growth restriction in pregnant women with systemic lupus erythematosus: a descriptive cohort study.Lupus. 2015 Nov;24(13):1384-91. doi: 10.1177/0961203315591027. Epub 2015 Jun 16. Lupus. 2015. PMID: 26082465
-
Cumulative dose of hydroxychloroquine is associated with a decrease of resting heart rate in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a pilot study.Lupus. 2015 Oct;24(11):1204-9. doi: 10.1177/0961203315580870. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Lupus. 2015. PMID: 25852050
-
Hydroxychloroquine in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017 Mar;16(3):411-419. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2017.1269168. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017. PMID: 27927040 Review.
-
Hydroxychloroquine prophylaxis for preeclampsia, hypertension and prematurity in pregnant patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A meta-analysis.Lupus. 2021 Jun;30(7):1163-1174. doi: 10.1177/09612033211007199. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Lupus. 2021. PMID: 33853420
Cited by
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus: updated insights on the pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention and therapeutics.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Mar 17;10(1):102. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02168-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40097390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the Pathophysiology of Preeclampsia: Exploring the Role of Antiphospholipid Antibodies and Future Directions.J Clin Med. 2024 May 2;13(9):2668. doi: 10.3390/jcm13092668. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38731197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Refractory autoimmune hemolytic anemia in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus and ulcerative colitis: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2024 May 6;12(13):2286-2292. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i13.2286. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 38808337 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tincani A, Dall'Ara F, Lazzaroni MG, Reggia R, Andreoli L. Pregnancy in patients with autoimmune disease: a reality in 2016. Autoimmun Rev. 2016;15(10):975‐977. - PubMed
-
- Whitelaw DA, Hall D, Kotze T. Pregnancy in systemic lupus erythematosus: a retrospective study from a developing community. Clin Rheumatol. 2008;27(5):577‐580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

