Association Between Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Results from the TCLSIH Cohort Study
- PMID: 37904787
- PMCID: PMC10613407
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S431049
Association Between Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Results from the TCLSIH Cohort Study
Abstract
Purpose: The prevalence of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in the general Chinese adult male population has risen sharply over the past few decades. Increasing evidence suggests that inflammation plays an important role in the pathogenesis of BPH. To better understand the role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of BPH, we can use the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) because it is a simple and effective marker of inflammation and immunity. This study aims to prospectively investigate the association between NLR levels and the prevalence of BPH in a general Chinese adult male population.
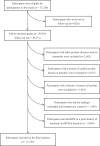
Patients and methods: This study included a total of 15,783 male participants free from BPH at baseline. NLR was measured according to the complete blood count. BPH was defined as total prostate volume (TPV) ≥30 mL, and TPV was determined by transabdominal ultrasonography. Multivariable Cox proportional hazards models were fitted to calculate hazards ratios (HRs) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for BPH risk with NLR levels.
Results: During a median follow-up of 2.7 years, 5078 BPH cases were documented. After adjusting for age, body mass index, smoking, alcohol, education, occupation, income, physical activity, total energy intake, personal and family history of disease, and inflammation markers, the multivariable-adjusted HRs of BPH were 1.00 (reference), 1.08 (95% CIs 0.99, 1.17), 1.10 (95% CIs1.02, 1.19), and 1.12 (95% CIs1.03, 1.21), respectively, for participants with NLR in the first, second, third, and fourth quartiles (P for trend <0.01).
Conclusion: Higher NLR levels were associated with a higher risk of BPH in Chinese adult male population. Our findings support the notion that NLR levels may be an important target for BPH prevention and intervention.
Keywords: benign prostatic hyperplasia; inflammation; neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; prospective cohort study.
© 2023 Song et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship between complete blood cell count-derived inflammatory biomarkers and benign prostatic hyperplasia in middle-aged and elderly individuals in the United States: Evidence from NHANES 2001-2008.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 9;19(7):e0306860. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306860. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38980876 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Mean Platelet Volume and Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Population Study from the TCLSIH Cohort Study.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Aug 5;16:3259-3269. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S416404. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37564954 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis.Urol Int. 2021;105(9-10):811-816. doi: 10.1159/000512894. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Urol Int. 2021. PMID: 33508844
-
Association between neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and depressive symptoms among Chinese adults: A population study from the TCLSIH cohort study.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019 May;103:76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2019.01.007. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2019. PMID: 30658341
-
The controversial relationship between benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer: the role of inflammation.Eur Urol. 2011 Jul;60(1):106-17. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.03.055. Epub 2011 Apr 9. Eur Urol. 2011. PMID: 21497433 Review.
Cited by
-
The relationship between complete blood cell count-derived inflammatory biomarkers and benign prostatic hyperplasia in middle-aged and elderly individuals in the United States: Evidence from NHANES 2001-2008.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 9;19(7):e0306860. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306860. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38980876 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Immune-Inflammatory Indexes and the Severity of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms/Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Cross-Sectional Study at a Tertiary Hospital in China.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jun 27;18:8509-8523. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S523193. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40599693 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous