Research progress of Claudin-low breast cancer
- PMID: 37904877
- PMCID: PMC10613467
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1226118
Research progress of Claudin-low breast cancer
Abstract
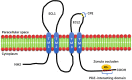
Claudin-low breast cancer (CLBC) is a subgroup of breast cancer discovered at the molecular level in 2007. Claudin is one of the primary proteins that make up tight junctions, and it plays crucial roles in anti-inflammatory and antitumor responses as well as the maintenance of water and electrolyte balance. Decreased expression of claudin results in the disruption of tight junction structures and the activation of downstream signaling pathways, which can lead to tumor formation. The origin of Claudin-low breast cancer is still in dispute. Claudin-low breast cancer is characterized by low expression of Claudin3, 4, 7, E-cadherin, and HER2 and high expression of Vimentin, Snai 1/2, Twist 1/2, Zeb 1/2, and ALDH1, as well as stem cell characteristics. The clinical onset of claudin-low breast cancer is at menopause age, and its histological grade is higher. This subtype of breast cancer is more likely to spread to lymph nodes than other subtypes. Claudin-low breast cancer is frequently accompanied by increased invasiveness and a poor prognosis. According to a clinical retrospective analysis, claudin-low breast cancer can achieve low pathological complete remission. At present, although several therapeutic targets of claudin-low breast cancer have been identified, the effective treatment remains in basic research stages, and no animal studies or clinical trials have been designed. The origin, molecular biological characteristics, pathological characteristics, treatment, and prognosis of CLBC are extensively discussed in this article. This will contribute to a comprehensive understanding of CLBC and serve as the foundation for the individualization of breast cancer treatment.
Keywords: Claudin-low; breast cancer; epithelial-mesenchymal transformation; immunohistochemistry; mammary stem cells.
Copyright © 2023 Pan, Xu, Ma, Yao, Zhao, Wang and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
BRCA Mutation-Related and Claudin-Low Breast Cancer: Blood Relatives or Stepsisters.Pathobiology. 2016;83(1):1-12. doi: 10.1159/000439135. Epub 2015 Nov 14. Pathobiology. 2016. PMID: 26566278
-
Lunatic Fringe and p53 Cooperatively Suppress Mesenchymal Stem-Like Breast Cancer.Neoplasia. 2017 Nov;19(11):885-895. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.08.006. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Neoplasia. 2017. PMID: 28938159 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinicopathologic and prognosis features of Claudin-low breast cancers].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2017 Sep 8;46(9):634-639. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5807.2017.09.009. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28910875 Chinese.
-
[Is there a claudin-low phenotype of breast cancer?].Arkh Patol. 2022;84(1):45-49. doi: 10.17116/patol20228401145. Arkh Patol. 2022. PMID: 35166478 Review. Russian.
-
Role of tight junctions in the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of cancer cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2021 Mar 1;1863(3):183503. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2020.183503. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2021. PMID: 33189716 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into E-Cadherin Impairment in CDH1-Unaltered Invasive Lobular Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Bioinformatic Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 17;25(16):8961. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168961. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201647 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial molecular profiling of mixed invasive ductal and lobular breast cancers reveals heterogeneity in intrinsic molecular subtypes, oncogenic signatures, and mutations.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 30;121(31):e2322068121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2322068121. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39042692 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysics of claudin proteins in tight junction architecture: Three decades of progress.Biophys J. 2024 Aug 20;123(16):2363-2378. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.06.010. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Biophys J. 2024. PMID: 38859584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Therapy in Breast Cancer: Advantages and Advancements of Antibody-Drug Conjugates, a Type of Chemo-Biologic Hybrid Drugs.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Oct 17;16(20):3517. doi: 10.3390/cancers16203517. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Landscape of lncRNAs expressed in Mexican patients with triple‑negative breast cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2025 Jun;31(6):163. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13528. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40211710 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

