The epithelial Na+ channel UNC-8 promotes an endocytic mechanism that recycles presynaptic components to new boutons in remodeling neurons
- PMID: 37906594
- PMCID: PMC10921563
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113327
The epithelial Na+ channel UNC-8 promotes an endocytic mechanism that recycles presynaptic components to new boutons in remodeling neurons
Abstract
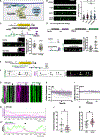
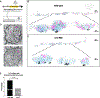
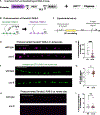
Circuit refinement involves the formation of new presynaptic boutons as others are dismantled. Nascent presynaptic sites can incorporate material from recently eliminated synapses, but the recycling mechanisms remain elusive. In early-stage C. elegans larvae, the presynaptic boutons of GABAergic DD neurons are removed and new outputs established at alternative sites. Here, we show that developmentally regulated expression of the epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) UNC-8 in remodeling DD neurons promotes a Ca2+ and actin-dependent mechanism, involving activity-dependent bulk endocytosis (ADBE), that recycles presynaptic material for reassembly at nascent DD synapses. ADBE normally functions in highly active neurons to accelerate local recycling of synaptic vesicles. In contrast, we find that an ADBE-like mechanism results in the distal recycling of synaptic material from old to new synapses. Thus, our findings suggest that a native mechanism (ADBE) can be repurposed to dismantle presynaptic terminals for reassembly at new, distant locations.
Keywords: C. elegans; CP: Cell biology; CP: Neuroscience; DEG/ENaC; bulk endocytosis; circuit refinement; synaptic remodeling.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

