Denosumab-Induced Rebound Hypercalcemia Treated With Bisphosphonates in a Pediatric Patient
- PMID: 37908209
- PMCID: PMC10612474
- DOI: 10.1210/jcemcr/luad133
Denosumab-Induced Rebound Hypercalcemia Treated With Bisphosphonates in a Pediatric Patient
Abstract
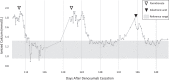
Denosumab is a RANK-L inhibitor used off-label as a treatment for a variety of pediatric bone disorders, including aneurysmal bone cysts (ABC). Rebound hypercalcemia is a known side effect after denosumab therapy and is more commonly reported in pediatric patients. Although there are no established treatment guidelines, denosumab-induced rebound hypercalcemia is usually managed with a combination of intravenous fluids, diuretics, corticosteroids, denosumab, and/or bisphosphonates. We present the case of a 10-year-old female patient with history of a right sacral ABC treated with denosumab who presented with recurrent episodes of rebound hypercalcemia beginning 3 months after denosumab cessation. After the third hospitalization for hypercalcemia, which was treated with zoledronic acid, normocalcemia was achieved. This case demonstrates an increasingly recognized side effect of denosumab therapy that occurs mainly in skeletally immature patients and presents a possible approach to initial therapy of rebound hypercalcemia with a long-acting bisphosphonate.
Keywords: aneurysmal bone cyst; denosumab; rebound hypercalcemia; zoledronic acid.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- Maximen J, Robin F, Tronchot A, Rossetti A, Ropars M, Guggenbuhl P. Denosumab in the management of Aneurysmal bone cyst. Joint Bone Spine. 2022;89(1):105260. - PubMed
-
- Deodati A, Fintini D, Levtchenko E, et al. . Mechanisms of acute hypercalcemia in pediatric patients following the interruption of Denosumab. J Endocrinol Invest. 2022;45(1):159‐166. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources