Teprotumumab for Treatment of Pretibial Myxedema
- PMID: 37908268
- PMCID: PMC10578414
- DOI: 10.1210/jcemcr/luac037
Teprotumumab for Treatment of Pretibial Myxedema
Abstract
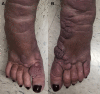
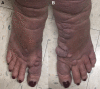
Pretibial myxedema (PTM), also called thyroid dermopathy, is a dreaded and potentially debilitating manifestation of thyroid disease, more commonly Graves' disease, which can occur at any time over the course of the disease. No substantial long-term therapies have been able to target the condition, and management has typically been supportive (eg, compression socks, weight loss), with courses of moderate-intensity steroids. Teprotumumab has been approved for the management of thyroid eye disease (TED), and it is believed that the 2 share a similar pathophysiology likely related to type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor, which may explain why some patients have also experienced improvement in PTM. Here we present a patient who received 8 doses of teprotumumab for TED who, over the course of management and into follow-up, experienced significant improvement in her pretibial myxedema. The patient noted considerable improvement in quality of life and ability to perform daily activities. We present this case to consider further investigation into the utilization of teprotumumab for thyroid disease-related PTM in patients with impaired quality of life.
Keywords: pretibial myxedema; teprotumumab; thyroid eye disease.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures

References
-
- Heymann WR. Teprotumumab: an eye-opening advance for pretibial myxedema? Accessed August 15, 2022. https://www.aad.org/dw/dw-insights-and-inquiries/medical-dermatology/tep...
-
- Kossler A, Martin Sears C, Dosiou C. Hearing loss and teprotumumab. J Endocrine Soc. 2021;5(Suppl 1):A839.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
