Recurrent Hypoglycemia Secondary to Insulinoma in an Adult With Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome
- PMID: 37908580
- PMCID: PMC10580426
- DOI: 10.1210/jcemcr/luad062
Recurrent Hypoglycemia Secondary to Insulinoma in an Adult With Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome
Abstract
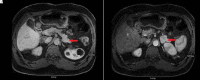
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by genetic and epigenetic changes on the chromosome 11p15.5 region, which includes genes that are important for fetal and postnatal growth. Children with BWS have a higher chance of having hypoglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, and malignancies early in life, although hypoglycemia caused by an insulinoma that develops later in life has not been reported. We describe the diagnosis of insulinoma in a 53-year-old man with BWS in this case report. This is the first case report of insulinoma in an adult with this syndrome.
Keywords: beckwith-wiedemann syndrome; heart failure; hyperinsulinemia; hypoglycemia; insulinoma.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures

References
-
- Hussain K, Cosgrove KE, Shepherd RM, et al. . Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome due to defects in the function of pancreatic beta-cell adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(7):4376‐4382. - PubMed
-
- Johannessen LE, Panagopoulos I, Haugvik SP, Gladhaug IP, Heim S, Micci F. Upregulation of INS-IGF2 read-through expression and identification of a novel INS-IGF2 splice variant in insulinomas. Oncol Rep. 2016;36(5):2653‐2662. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
