A False Pituitary Tumor
- PMID: 37908583
- PMCID: PMC10580463
- DOI: 10.1210/jcemcr/luad054
A False Pituitary Tumor
Abstract
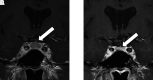
A false pituitary tumor describes pituitary enlargement due to intracranial hypotension. Reported previously primarily in the neurological literature, we present this case referred to endocrinology for evaluation of a pituitary mass. A 24-year-old male was referred to endocrinology for evaluation of pituitary enlargement without a hypo-enhancing lesion on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The main symptom reported was headache that was worse in the standing position and in the afternoon. He had no symptoms or signs of pituitary mass-effect, or hormone excess or deficiencies. Past medical history was relevant for a history of nerve schwannoma status post resection with subsequent spinal fusion. Biochemical evaluation of pituitary hormones was normal. Upon review of his pituitary MRI, other abnormalities seen were suggestive of intracranial hypotension. Based on his history and imaging findings, he was diagnosed with intracranial hypotension causing a "false pituitary tumor" rather than pituitary enlargement or abnormality. Further evaluation revealed multiple spinal leaks that were patched. His symptoms subsided within a few days of repair. Endocrinologists should be aware of the possible misdiagnosis of a pituitary mass due to intracranial hypotension.
Keywords: CSF leak; intracranial hypotension; pituitary tumor.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures

References
-
- Jagannathan J, Kanter AS, Sheehan JP, Jane JA Jr, Laws ER Jr. Benign brain tumors: sellar/parasellar tumors. Neurol Clin. 2007;25(4):1231‐49, xi. - PubMed
-
- MacFarlane J, Bashari WA, Senanayake R, et al. . Advances in the imaging of pituitary tumors. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2020;49(3):357‐373. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
