The role of radiolabeling in BNCT tracers for enhanced dosimetry and treatment planning
- PMID: 37908724
- PMCID: PMC10614688
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.88998
The role of radiolabeling in BNCT tracers for enhanced dosimetry and treatment planning
Abstract
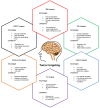
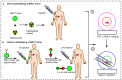
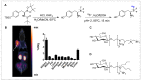
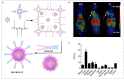
Positron emission tomography (PET) and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) are potent technologies for non-invasive imaging of pharmacological and biochemical processes in both preclinical and advanced clinical research settings. In the field of radiation therapy, boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) stands out because it harnesses biological mechanisms to precisely target tumor cells while preserving the neighboring healthy tissues. To achieve the most favorable therapeutic outcomes, the delivery of boron-enriched tracers to tumors must be selective and efficient, with a substantial concentration of boron atoms meticulously arranged in and around the tumor cells. Although several BNCT tracers have been developed to facilitate the targeted and efficient delivery of boron to tumors, only a few have been labeled with PET or SPECT radionuclides. Such radiolabeling enables comprehensive in vivo examination, encompassing crucial aspects such as pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, tumor selectivity, and accumulation and retention of the tracer within the tumor. This review provides a comprehensive summary of the essential aspects of BNCT tracers, focusing on their radiolabeling with PET or SPECT radioisotopes. This leads to more effective and targeted treatment approaches which ultimately enhance the quality of patient care with respect to cancer treatment.
Keywords: BNCT; PET; SPECT; radiolabeling; theranostics, targeted therapy.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures








References
-
- Hawthorne MF. The role of chemistry in the development of boron neutron capture therapy of cancer. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1993;32(7):950–84.
-
- Barth RF, Coderre JA, Vicente MG, Blue TE. Boron neutron capture therapy of cancer: current status and future prospects. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(11):3987–4002. - PubMed
-
- Lakshminarayana G, Kebaili I, Dong MG, Al-Buriahi MS, Dahshan A, Kityk IV. et al. Estimation of gamma-rays, and fast and the thermal neutrons attenuation characteristics for bismuth tellurite and bismuth boro-tellurite glass systems. J Mater Sci. 2020;55:5750–71.
-
- Hirase S, Aoki A, Hattori Y, Morimoto K, Noguchi K, Fujii I. et al. Dodecaborate-encapsulated extracellular vesicles with modification of cell-penetrating peptides for enhancing macropinocytotic cellular uptake and biological activity in boron neutron capture therapy. Mol Pharm. 2022;19(4):1135–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

