Gold-Induced Cytokine (GOLDIC®) Therapy in the Management of Knee Osteoarthritis: An Observational Study
- PMID: 37908900
- PMCID: PMC10613552
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.46231
Gold-Induced Cytokine (GOLDIC®) Therapy in the Management of Knee Osteoarthritis: An Observational Study
Erratum in
-
Correction: Gold-Induced Cytokine (GOLDIC®) Therapy in the Management of Knee Osteoarthritis: An Observational Study.Cureus. 2023 Oct 13;15(10):c138. doi: 10.7759/cureus.c138. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38348280 Free PMC article.
-
Correction: Gold-Induced Cytokine (GOLDIC®) Therapy in the Management of Knee Osteoarthritis: An Observational Study.Cureus. 2023 Oct 9;15(10):c136. doi: 10.7759/cureus.c136. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38348283 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Current treatment modalities for knee osteoarthritis (OA) provide symptomatic cures rather than reversing the pathology in the long term. An innovative regenerative therapy called "Gold Induced Cytokines" (GOLDIC®) was explored in various musculoskeletal diseases such as knee OA, lumbar canal stenosis, Achilles tendinopathy, and plantar fasciitis. In this study, we explored the safety and functional outcome of GOLDIC® injections in knee OA (KL grades 3 and 4) with visual analog scale (VAS) and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) scores.
Materials and methods: A multi-center open-label observational study was carried out after screening the cases according to the inclusion criteria. A total of 106 knees in 65 patients were enrolled for four doses of 4 ml of ultrasound-guided intra-articular GOLDIC® injections every three to six days. All cases were followed up with pre- and post-VAS and WOMAC scores at an interval of four weeks, three months, six months, and one year, and the complications (including severe adverse reactions) were monitored throughout.
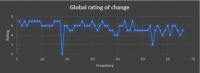
Results: In this study, 66.1% had grade 4 OA knee (without gross varus or subluxation) and 33.8% had grade 3 OA knee. All the participants underwent the GOLDIC® treatment modality. A statistically significant difference was observed in pre- and post-procedural follow-up in VAS and WOMAC scores at one-year follow-up. There were no recorded severe adverse reactions during the entire study period. Three patients failed the treatment in one year.
Conclusion: The GOLDIC® procedure shows great promise as a novel method for treating moderate to severe OA of the knee, both in terms of pain and functional outcome without any severe adverse reactions, in a sustained manner and is worth exploring as a long-term treatment option.
Keywords: cytokines; gelsolin; gold; knee; osteoarthritis.
Copyright © 2023, Tulpule et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared financial relationships, which are detailed in the next section.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Gold-Induced Cytokine (GOLDIC) for the Management of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Nov 5;16(11):e73040. doi: 10.7759/cureus.73040. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39640134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intra-articular gold induced cytokine (GOLDIC®) injection therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of knee joint: a clinical study.Int Orthop. 2021 Feb;45(2):497-507. doi: 10.1007/s00264-020-04870-w. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Int Orthop. 2021. PMID: 33404700 Clinical Trial.
-
Role of Triple Injection Platelet-Rich Plasma for Osteoarthritis Knees: A 2 Years Follow-Up Study.Indian J Orthop. 2021 Jul 29;56(2):249-255. doi: 10.1007/s43465-021-00459-6. eCollection 2022 Feb. Indian J Orthop. 2021. PMID: 35140855 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Functional Outcome of Single Versus Multiple Intra-articular Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection for Early Osteoarthritis Knee.Cureus. 2023 May 3;15(5):e38513. doi: 10.7759/cureus.38513. eCollection 2023 May. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37273322 Free PMC article.
-
The Therapeutic Effect of Intra-articular Normal Saline Injections for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Meta-analysis of Evidence Level 1 Studies.Am J Sports Med. 2017 Sep;45(11):2647-2653. doi: 10.1177/0363546516680607. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Am J Sports Med. 2017. PMID: 28027657 Review.
Cited by
-
Autologous peripheral blood-derived orthobiologics: Different types and their effectiveness in managing knee osteoarthritis.World J Orthop. 2024 May 18;15(5):400-403. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v15.i5.400. eCollection 2024 May 18. World J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 38835681 Free PMC article.
-
Current Non-Surgical Curative Regenerative Therapies for Knee Osteoarthritis.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024 Nov;20(8):2104-2123. doi: 10.1007/s12015-024-10768-6. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024. PMID: 39145857 Review.
-
Autologous Growth Factor-Rich Concentrate (GFC) Injection in Non-union of Fractures: A Quasi-experimental Study.Indian J Orthop. 2024 Oct 5;58(12):1833-1843. doi: 10.1007/s43465-024-01278-1. eCollection 2024 Dec. Indian J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39664350
-
GOLDIC Therapy Holds Promise as an Orthobiologic Agent: A Systematic Review of the Literature.Indian J Orthop. 2024 May 7;58(7):858-865. doi: 10.1007/s43465-024-01167-7. eCollection 2024 Jul. Indian J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 38948367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gold-Induced Cytokine (GOLDIC) for the Management of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Nov 5;16(11):e73040. doi: 10.7759/cureus.73040. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39640134 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Evidence-based status of microfracture technique: a systematic review of level I and II studies. Goyal D, Keyhani S, Lee EH, Hui JH. Arthroscopy. 2013;29:1579–1588. - PubMed
-
- The response of articular cartilage to mechanical injury. Mankin HJ. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6174527/ J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64:460–466. - PubMed
-
- Projections of US prevalence of arthritis and associated activity limitations. Hootman JM, Helmick CG. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:226–229. - PubMed
-
- Osteoarthritis year 2010 in review: non-pharmacologic therapy. Hawker GA, Mian S, Bednis K, Stanaitis I. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19:366–374. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
