Evaluation of the effect of Matricaria recutita monotherapy or in combination with photodynamic therapy on tissue repair in the dorsum of the tongue of rats
- PMID: 37909526
- PMCID: PMC10609644
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-7757-2023-0211
Evaluation of the effect of Matricaria recutita monotherapy or in combination with photodynamic therapy on tissue repair in the dorsum of the tongue of rats
Abstract
Objective: The search for treatments that accelerate the healing of lesions is of constant interest. Matricaria recutita (chamomile) is a plant with antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and healing properties, and antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy (aPDT) eradicates microorganisms, which favors tissue repair. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of the topical use of chamomile with or without aPDT on tissue repair in rats' tongues.
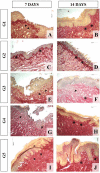
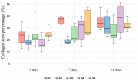
Methodology: A total of 75 male Wistar rats underwent standardized ulceration on the dorsum of the tongue using a punch of 5 mm diameter and were randomly allocated into the following groups: control (G1), chamomile fluid extract (G2), chamomile infusion (G3), aPDT (G4), and chamomile infusion + aPDT (G5). On the 3rd, 7th, and 14th days postoperatively, euthanasia was performed, and the ulcers were measured using calipers. The presence of edema, inflammatory infiltrate, cellularity, re-epithelialization, and characterization of total collagen were evaluated using sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin and Red Sirius. Histomorphometry analyses of the percentage of total collagen, the distance from the basal layer to the epithelial surface, and the thickness of the stratum corneum were performed. Descriptive (absolute/relative frequencies and modes) and exploratory analyses were performed. The associations between the groups and the presence of ulcers were analyzed with Fisher's exact test. All analyses were performed using the R program and statistical significance was set at p=0.05.
Results: The G2 positively modulated the exudative and proliferative phases of repair, both clinically (p<0.0001) and histologically, whether in descriptive or inferential analyses (p<0.05). The G3 showed a significant difference in clinical parameters compared with G1 (p<0.0001). The G4 and G5 did not positively modulate tissue repair.
Conclusion: The chamomile fluid extract showed better outcomes for tissue repair in the rat tongue.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the use of chamomile in isolation and in association with laser photobiomodulation in the healing of rats oral mucosa.Photochem Photobiol. 2024 Sep-Oct;100(5):1431-1445. doi: 10.1111/php.13901. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Photochem Photobiol. 2024. PMID: 38240454
-
Effects of Chamomilla recutita (L.) on oral wound healing in rats.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011 Sep 1;16(6):e716-21. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011. PMID: 21196867
-
TNF-alpha expression, evaluation of collagen, and TUNEL of Matricaria recutita L. extract and triamcinolone on oral ulcer in diabetic rats.J Appl Oral Sci. 2016 May-Jun;24(3):278-90. doi: 10.1590/1678-775720150481. J Appl Oral Sci. 2016. PMID: 27383710 Free PMC article.
-
A review of the bioactivity and potential health benefits of chamomile tea (Matricaria recutita L.).Phytother Res. 2006 Jul;20(7):519-30. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1900. Phytother Res. 2006. PMID: 16628544 Review.
-
Chamomile: A systematic review of adverse events.Complement Ther Med. 2025 Aug;91:103192. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2025.103192. Epub 2025 May 13. Complement Ther Med. 2025. PMID: 40374153
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

