Dexmedetomidine Preconditioning Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Suppressing Mitophagy Via Activating Α2-Adrenergic Receptor
- PMID: 37909577
- PMCID: PMC12080598
- DOI: 10.36660/abc.20220750
Dexmedetomidine Preconditioning Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Suppressing Mitophagy Via Activating Α2-Adrenergic Receptor
Abstract
Background: Dexmedetomidine (DEX), a specific α2-adrenergic receptor agonist, is protective against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (MIRI). However, the association between DEX preconditioning-induced cardioprotection and mitophagy suppression remains unclear.
Objective: Hence, we aimed to investigate whether DEX preconditioning alleviates MIRI by suppressing mitophagy via α2-adrenergic receptor activation.
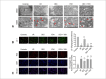
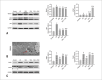
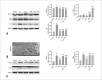
Method: Sixty isolated rat hearts were treated with or without DEX before inducing ischemia and reperfusion; an α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist, yohimbine (YOH), was also administered before ischemia, alone or with DEX. The heart rate (HR), left ventricular diastolic pressure (LVDP), left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP), maximal and minimal rate of left ventricular pressure development (±dp/dtmax), and myocardial infarction size were measured. The mitochondrial ultrastructure and autophagosomes were assessed using transmission electron microscopy. Mitochondrial membrane potential and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels were measured using JC-1 and dichloride hydrofluorescein diacetate assays, respectively. The expression levels of the mitophagy-associated proteins Beclin1, LC3II/I ratio, p62, PINK1, and Parkin were detected by western blotting.
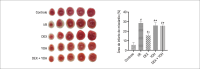
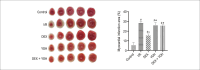
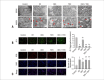
Results: Compared with the control group, in the ischemia/reperfusion group, the HR, LVDP, and ±dp/dtmax were remarkably decreased (p< 0.05), whereas LVEDP and infarct sizes were significantly increased (p< 0.05). DEX preconditioning significantly improved cardiac dysfunction reduced myocardial infarction size, maintained mitochondrial structural integrity, increased mitochondrial membrane potential, inhibited autophagosomes formation, and decreased ROS production and Beclin1, LC3II/I ratio, PINK1, Parkin, and p62 expression(p< 0.05). When DEX and YOH were combined, YOH canceled the effect of DEX, whereas the use of YOH alone had no effect.
Conclusion: Therefore, DEX preconditioning was cardioprotective against MIRI in rats by suppressing mitophagy via α2-adrenergic receptor activation.
Fundamento: A dexmedetomidina (DEX), um agonista específico do receptor α2-adrenérgico, é protetora contra lesão de isquemia/reperfusão miocárdica (I/R). No entanto, a associação entre a cardioproteção induzida pelo pré-condicionamento DEX e a supressão da mitofagia permanece pouco clara.
Objetivo: Portanto, nosso objetivo foi investigar se o pré-condicionamento com DEX alivia a I/R, suprimindo a mitofagia via ativação do receptor α2-adrenérgico.
Método: Sessenta corações de ratos isolados foram tratados com ou sem DEX antes de induzir isquemia e reperfusão; um antagonista do receptor α2-adrenérgico, a ioimbina (YOH), também foi administrado antes da isquemia, isoladamente ou com DEX. A frequência cardíaca (FC), pressão diastólica do ventrículo esquerdo (PDVE), pressão diastólica final do ventrículo esquerdo (PDFVE), taxa máxima e mínima de desenvolvimento da pressão ventricular esquerda (±dp/dtmax) e tamanho do infarto do miocárdio foram medidos. A ultraestrutura mitocondrial e as autofagossomas foram avaliadas por microscopia eletrônica de transmissão. O potencial de membrana mitocondrial e os níveis de espécies reativas de oxigênio (ROS) foram medidos usando os ensaios JC-1 e diacetato de diclorodi hidrofluoresceína, respectivamente. Os níveis de expressão das proteínas associadas à mitofagia Beclin1, relação LC3II/I, p62, PINK1 e Parkin foram detectados por western blotting.
Resultados: Em comparação com o grupo controle, no grupo isquemia/reperfusão, a FC, PDVE e ±dp/dtmax foram notavelmente diminuídas (p<0,05), enquanto os tamanhos da PDFVE e do infarto aumentaram significativamente (p<0,05). O pré-condicionamento com DEX melhorou significativamente a disfunção cardíaca, reduziu o tamanho do infarto do miocárdio, manteve a integridade estrutural mitocondrial, aumentou o potencial de membrana mitocondrial, inibiu a formação de autofagossomas e diminuiu a produção de ROS e a relação Beclin1, relação LC3II/I, expressão PINK1, Parkin e p62(p<0,05). Quando DEX e YOH foram combinados, o YOH cancelou o efeito da DEX, enquanto o uso de YOH sozinha não teve efeito.
Conclusão: Portanto, o pré-condicionamento DEX foi cardioprotetor contra I/R em ratos, suprimindo a mitofagia por meio da ativação do receptor α2-adrenérgico.
Conflict of interest statement
Potencial conflito de interesse
Não há conflito com o presente artigo
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

