Efficacy of ClinproTMXT Varnish surrounding brackets on the enamel surface of white spot lesion
- PMID: 37909637
- PMCID: PMC10642276
- DOI: 10.1590/0103-6440202305405
Efficacy of ClinproTMXT Varnish surrounding brackets on the enamel surface of white spot lesion
Abstract
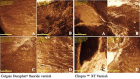
Orthodontics patients usual develop demineralization and present cavity caries lesions after six months. Minimally invasive procedures have been the goal in modern dental practice. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of ClinproTMXT Varnish, on the enamel surface roughness and severity of white spot lesions. Twenty premolars were submitted to bond brackets and experimental induction of demineralization and randomly divided into 2 groups: GI - fluoride varnish (Colgate Duraphat®); GII - Ionomeric Sealant (ClinproTMXT Varnish). The treatment was applied around the brackets. The surface roughness of specimens was analyzed, before treatment and 12 weeks after treatment by laser confocal microscopy, and the severity of the white spot lesion was by laser fluorescence device. The data were analyzed by non-parametric Wilcoxon and Mann-Whitney Test, at 5% significance, roughness percentage reduction was performed. The severity of demineralization decreased in both, GI (p = 0.005) and GII (p = 0.019). Enamel superficial roughness levels decreased in GI and GII. As well as the roughness percentage, being more expressive in the ClinproTMXT Varnish group (85,09%). Colgate Duraphat® or Clinpro™ XT Varnish reduced the severity of the demineralization and decreased the superficial roughness on the enamel. The Clinpro™ XT Varnish was superior to superficial roughness on enamel.
Pacientes ortodônticos geralmente desenvolvem desmineralização e apresentam lesões de cárie após seis meses de tratamento. Procedimentos minimamente invasivos têm sido o objetivo na prática odontológica moderna. O objetivo deste estudo foi avaliar o efeito do ClinproTM XT selante ionomérico, ao redor do bráquete, com relação a rugosidade superficial do esmalte e a severidade da lesão induzida. Vinte pré-molares foram submetidos a colagem de bráquetes e indução experimental de desmineralização e divididos aleatoriamente em 2 grupos: GI - verniz fluoretado (Colgate Duraphat®); GII - Selante Ionomérico (ClinproTM XT). O tratamento foi aplicado ao redor dos bráquetes. A rugosidade da superfície dos espécimes foi analisada, antes do tratamento e 12 semanas após o tratamento por microscopia confocal a laser e severidade da lesão de mancha branca por dispositivo de fluorescência a laser. Os dados foram analisados pelo teste não paramétrico de Wilcoxon e Mann-Whitney, a 5% de significância. A taxa de redução da lesão foi calculada. A severidade da desmineralização diminuiu tanto no GI (p = 0,005) quanto no GII (p = 0,019). Os níveis de rugosidade superficial do esmalte diminuíram no GI e GII, assim como o percentual de rugosidade, sendo mais expressivo no grupo ClinproTMXT (85,09%). Colgate Duraphat® e Clinpro™ XT reduziram a severidade da desmineralização e diminuíram a rugosidade superficial do esmalte. O selante ionomérico Clinpro™ XT foi superior na redução percentual de rugosidade.
Figures


References
-
- Seow WK. Early Childhood Caries. Pediatr. Clin. NA. 2018;65(5):941–954. - PubMed
-
- Fernando S, Tadakamadla SK, Bakr M, Scuffham PA, Johnson NW. Indicators of Risk for Dental Caries in Children: A Holistic Approach. JDR Clin Trans Res. 2019;4(4):333–341. - PubMed
-
- Tasios T, Haidich AB. Prevention of orthodontic enamel demineralization: A systematic review with meta ‚Äê analyses. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2019;4(4):333–341. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

