Carbon-to-nitrogen single-atom transmutation of azaarenes
- PMID: 37914946
- PMCID: PMC10907950
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06613-4
Carbon-to-nitrogen single-atom transmutation of azaarenes
Abstract
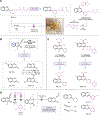
When searching for the ideal molecule to fill a particular functional role (for example, a medicine), the difference between success and failure can often come down to a single atom1. Replacing an aromatic carbon atom with a nitrogen atom would be enabling in the discovery of potential medicines2, but only indirect means exist to make such C-to-N transmutations, typically by parallel synthesis3. Here, we report a transformation that enables the direct conversion of a heteroaromatic carbon atom into a nitrogen atom, turning quinolines into quinazolines. Oxidative restructuring of the parent azaarene gives a ring-opened intermediate bearing electrophilic sites primed for ring reclosure and expulsion of a carbon-based leaving group. Such a 'sticky end' approach subverts existing atom insertion-deletion approaches and as a result avoids skeleton-rotation and substituent-perturbation pitfalls common in stepwise skeletal editing. We show a broad scope of quinolines and related azaarenes, all of which can be converted into the corresponding quinazolines by replacement of the C3 carbon with a nitrogen atom. Mechanistic experiments support the critical role of the activated intermediate and indicate a more general strategy for the development of C-to-N transmutation reactions.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


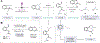
Comment in
-
Atom-swap chemistry could aid drug discovery.Nature. 2023 Nov;623(7985):36-37. doi: 10.1038/d41586-023-03297-8. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37914944 No abstract available.
References
-
- Pennington LD, Collier PN & Comer E Harnessing the necessary nitrogen atom in chemical biology and drug discovery. Med. Chem. Res. 10.1007/s00044-023-03073-3 (2023). - DOI
-
- Schönherr H & Cernak T Profound methyl effects in drug discovery and a call for new C–H methylation reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52, 12256–12267 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Chiodi D & Ishihara Y “Magic chloro”: profound effects of the chlorine atom in drug discovery. J. Med. Chem. 66, 5305–5331 (2023). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

