Characteristics and survival of patients with gynecological cancers who refuse radiotherapy: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 37915037
- PMCID: PMC10621229
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-023-02720-6
Characteristics and survival of patients with gynecological cancers who refuse radiotherapy: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Radiotherapy improves survival for many cancer patients. However, some patients still refuse radiotherapy despite the recommendations of their physicians. We aimed to investigate the impact of refusing recommended radiotherapy on overall survival in patients with gynecological cancers (GC) and attempted to describe what characteristics are associated with the refusal of radiotherapy.
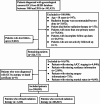
Methods: Data were extracted from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Result (SEER) database for patients who were diagnosed with GC and recommended for radiotherapy between 1988 and 2016. Kaplan-Meier and multivariate Cox regression analyses were utilized to analyze the impact of refusal of radiotherapy on overall survival. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to identify characteristics associated with refusal of radiotherapy.
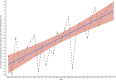
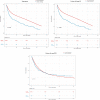
Results: In total, 1,226 of 208,093 patients (0.6%) refused radiotherapy. Multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that refusal of radiotherapy was associated with poorer overall survival in GC patients with stage I/II [hazard ratio (HR) = 1.64; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.50-1.79], but may not affect overall survival in patients with stage III/IV (HR = 1.03; 95%CI, 0.84-1.25). Multivariate logistic regression analysis demonstrated that factors such as older age (40-65 years, > 65 years), unmarried status (divorced, single, widowed), higher foreign-born rate (1.87-2.82%, 1.51-2.19), refusal of surgery (recommended but not performed), and higher grade (poorly differentiated, undifferentiated/anaplastic) may increase the likelihood of refusing radiotherapy (all P < 0.05). Factors that may reduce the likelihood of refusing radiotherapy include higher income (> 42,810$), lower grade (well-differentiated), primary site of ovarian cancer, and no/unknown chemotherapy (all P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Refusal of radiotherapy is related to worse overall survival in GC patients with stage I/II, and many characteristics may affect a patient's choice of refusal of radiotherapy.
Keywords: Gynecological cancers; Overall survival; Refusal of radiotherapy; Stage.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

