Beneficial effects of recombinant CER-001 high-density lipoprotein infusion in sepsis: results from a bench to bedside translational research project
- PMID: 37915050
- PMCID: PMC10621167
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-023-03057-5
Beneficial effects of recombinant CER-001 high-density lipoprotein infusion in sepsis: results from a bench to bedside translational research project
Abstract
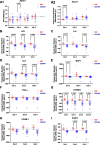
Background: Sepsis is characterized by a dysregulated immune response and metabolic alterations, including decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels. HDL exhibits beneficial properties, such as lipopolysaccharides (LPS) scavenging, exerting anti-inflammatory effects and providing endothelial protection. We investigated the effects of CER-001, an engineered HDL-mimetic, in a swine model of LPS-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) and a Phase 2a clinical trial, aiming to better understand its molecular basis in systemic inflammation and renal function.
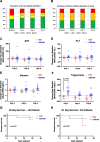
Methods: We carried out a translational approach to study the effects of HDL administration on sepsis. Sterile systemic inflammation was induced in pigs by LPS infusion. Animals were randomized into LPS (n = 6), CER20 (single dose of CER-001 20 mg/kg; n = 6), and CER20 × 2 (two doses of CER-001 20 mg/kg; n = 6) groups. Survival rate, endothelial dysfunction biomarkers, pro-inflammatory mediators, LPS, and apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I) levels were assessed. Renal and liver histology and biochemistry were analyzed. Subsequently, we performed an open-label, randomized, dose-ranging (Phase 2a) study included 20 patients with sepsis due to intra-abdominal infection or urosepsis, randomized into Group A (conventional treatment, n = 5), Group B (CER-001 5 mg/kg BID, n = 5), Group C (CER-001 10 mg/kg BID, n = 5), and Group D (CER-001 20 mg/kg BID, n = 5). Primary outcomes were safety and efficacy in preventing AKI onset and severity; secondary outcomes include changes in inflammatory and endothelial dysfunction markers.
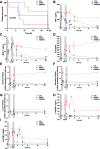
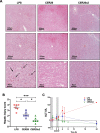
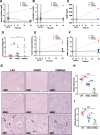
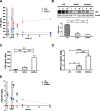
Results: CER-001 increased median survival, reduced inflammatory mediators, complement activation, and endothelial dysfunction in endotoxemic pigs. It enhanced LPS elimination through the bile and preserved liver and renal parenchyma. In the clinical study, CER-001 was well-tolerated with no serious adverse events related to study treatment. Rapid ApoA-I normalization was associated with enhanced LPS removal and immunomodulation with improvement of clinical outcomes, independently of the type and gravity of the sepsis. CER-001-treated patients had reduced risk for the onset and progression to severe AKI (stage 2 or 3) and, in a subset of critically ill patients, a reduced need for organ support and shorter ICU length of stay.
Conclusions: CER-001 shows promise as a therapeutic strategy for sepsis management, improving outcomes and mitigating inflammation and organ damage.
Trial registration: The study was approved by the Agenzia Italiana del Farmaco (AIFA) and by the Local Ethic Committee (N° EUDRACT 2020-004202-60, Protocol CER-001- SEP_AKI_01) and was added to the EU Clinical Trials Register on January 13, 2021.
Keywords: ApoA-I complexes; Cytokine storm; Multi-organ dysfunction; Sepsis.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
LG received research funding from Abionyx and Sanofi (Granted to his University Department), and received speaker and consultancy fees from Fresenius, Estor, Werfen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Travere, Sandoz, Baxter, Mundipharma, Pharmadoc, Retrophin, GSK, Novartis, and Chinook. CKP, RB, and CT are employees of Abionyx Pharma. MF received speaker fees from Estor. The remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Ronco C, Wald R, Martensson J, Maiden M, et al. Acute kidney injury in sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43(6):816–828. - PubMed
-
- Cruz DN, Antonelli M, Fumagalli R, Foltran F, Brienza N, Donati A, et al. Early use of polymyxin B hemoperfusion in abdominal septic shock: the EUPHAS randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2009;301(23):2445–2452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

