Understanding hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection subtleties
- PMID: 37915190
- PMCID: PMC10665629
- DOI: 10.5946/ce.2023.195
Understanding hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection subtleties
Conflict of interest statement
Diogo Turiani Hourneaux de Moura is currently serving as an associate editor in Clinical Endoscopy; however, he was not involved in the peer reviewer selection, evaluation, or decision process for this article. The authors have no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
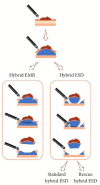


Comment on
-
Significance of rescue hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection in difficult colorectal cases.Clin Endosc. 2023 Nov;56(6):778-789. doi: 10.5946/ce.2022.268. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Clin Endosc. 2023. PMID: 37491992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yahagi N. Development of colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Endosc. 2022;34 Suppl 2:95–98. - PubMed
-
- Gotoda T, Kondo H, Ono H, et al. A new endoscopic mucosal resection procedure using an insulation-tipped electrosurgical knife for rectal flat lesions: report of two cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999;50:560–563. - PubMed
-
- Sagae VM, Ribeiro IB, de Moura DT, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection versus transanal endoscopic surgery for the treatment of early rectal tumor: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2020;34:1025–1034. - PubMed
-
- Turiani Hourneaux de Moura D, Aihara H, Jirapinyo P, et al. Robot-assisted endoscopic submucosal dissection versus conventional ESD for colorectal lesions: outcomes of a randomized pilot study in endoscopists without prior ESD experience (with video) Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;90:290–298. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

