Volitional activation of remote place representations with a hippocampal brain-machine interface
- PMID: 37917713
- PMCID: PMC10683874
- DOI: 10.1126/science.adh5206
Volitional activation of remote place representations with a hippocampal brain-machine interface
Abstract
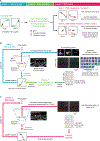
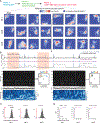
The hippocampus is critical for recollecting and imagining experiences. This is believed to involve voluntarily drawing from hippocampal memory representations of people, events, and places, including maplike representations of familiar environments. However, whether representations in such "cognitive maps" can be volitionally accessed is unknown. We developed a brain-machine interface to test whether rats can do so by controlling their hippocampal activity in a flexible, goal-directed, and model-based manner. We found that rats can efficiently navigate or direct objects to arbitrary goal locations within a virtual reality arena solely by activating and sustaining appropriate hippocampal representations of remote places. This provides insight into the mechanisms underlying episodic memory recall, mental simulation and planning, and imagination and opens up possibilities for high-level neural prosthetics that use hippocampal representations.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
T.D.H. is also affiliated with the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Johns Hopkins University.
Figures


References
-
- Schacter DL, Addis DR, Buckner RL, Remembering the past to imagine the future: the prospective brain. Nat Rev Neurosci. 8, 657–661 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Hamrick JB, Analogues of mental simulation and imagination in deep learning. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences 29, 8–16 (2019).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

