Massive invasion of organellar DNA drives nuclear genome evolution in Toxoplasma
- PMID: 37917792
- PMCID: PMC10636329
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2308569120
Massive invasion of organellar DNA drives nuclear genome evolution in Toxoplasma
Abstract
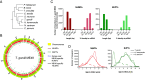
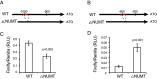
Toxoplasma gondii is a zoonotic protist pathogen that infects up to one third of the human population. This apicomplexan parasite contains three genome sequences: nuclear (65 Mb); plastid organellar, ptDNA (35 kb); and mitochondrial organellar, mtDNA (5.9 kb of non-repetitive sequence). We find that the nuclear genome contains a significant amount of NUMTs (nuclear integrants of mitochondrial DNA) and NUPTs (nuclear integrants of plastid DNA) that are continuously acquired and represent a significant source of intraspecific genetic variation. NUOT (nuclear DNA of organellar origin) accretion has generated 1.6% of the extant T. gondii ME49 nuclear genome-the highest fraction ever reported in any organism. NUOTs are primarily found in organisms that retain the non-homologous end-joining repair pathway. Significant movement of organellar DNA was experimentally captured via amplicon sequencing of a CRISPR-induced double-strand break in non-homologous end-joining repair competent, but not ku80 mutant, Toxoplasma parasites. Comparisons with Neospora caninum, a species that diverged from Toxoplasma ~28 mya, revealed that the movement and fixation of five NUMTs predates the split of the two genera. This unexpected level of NUMT conservation suggests evolutionary constraint for cellular function. Most NUMT insertions reside within (60%) or nearby genes (23% within 1.5 kb), and reporter assays indicate that some NUMTs have the ability to function as cis-regulatory elements modulating gene expression. Together, these findings portray a role for organellar sequence insertion in dynamically shaping the genomic architecture and likely contributing to adaptation and phenotypic changes in this important human pathogen.
Keywords: Coccidia; non-homologous end-joining repair—NHEJ; nuclear DNA of organellar origin—NUOT; nuclear integrants of mitochondrial DNA—NUMTs; nuclear integrants of plastid DNA—NUPTs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

Update of
-
Massive invasion of organellar DNA drives nuclear genome evolution in Toxoplasma.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 25:2023.05.22.539837. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.22.539837. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Nov 7;120(45):e2308569120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2308569120. PMID: 37293002 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Dubey J. P., Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans (CRC Press, ed. 3, 2021).
-
- Belanger F., Derouin F., Grangeot-keros L., Meyer L., Incidence and risk factors of toxoplasmosis in a cohort of human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients: 1988–1995. HEMOCO and SEROCO Study Groups. Clin. Infect. Dis. 28, 575–581 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Gilbert R. E., et al. , Effect of prenatal treatment on mother to child transmission of Toxoplasma gondii: Retrospective cohort study of 554 mother-child pairs in Lyon, France. Int. J. Epidemiol. 30, 1303–1308 (2001). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

