Advanced renal pelvis carcinoma patient with an ERBB2 insertion mutation: a case report
- PMID: 37917812
- PMCID: PMC10623987
- DOI: 10.1177/03000605231204502
Advanced renal pelvis carcinoma patient with an ERBB2 insertion mutation: a case report
Abstract
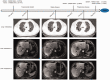
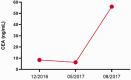
The prognosis of renal pelvis cancer is poor and therapeutic options are limited, especially for patients with advanced disease. In this report, we present a case of advanced renal pelvis carcinoma in a male patient in his 60s, characterized by an activating mutation in ERBB2. Clinical evaluation resulted in a pathological diagnosis of renal pelvis carcinoma with liver metastasis. Immunohistochemistry staining results suggested that CK, P63, and PAX8 were positively expressed, while Sy, CK7, CK20, S100, PAX8, and HEP1 were negatively expressed. Furthermore, next-generation sequencing results showed an activating mutation in the ERBB2 gene. The patient initially received a trastuzumab-based combination therapy, which led to a significant reduction in ERBB2 mutation frequency and a stable condition after three treatment cycles. However, following continuous treatment for 4 months, the patient developed drug resistance that resulted in disease relapse. Subsequently, the patient received apatinib treatment, but the therapeutic response was not satisfactory. The patient's condition underwent rapid deterioration and he ultimately succumbed to the disease. This case underscores the potential benefit of trastuzumab for treating ERBB2-mutated advanced renal pelvis cancer, but further highlights that overcoming drug resistance remains a crucial challenge for long-term efficacy.
Keywords: ERBB2 mutation; case report; drug resistance; metastasis; recurrence; renal pelvis cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Real-world association of HER2/ERBB2 concordance with trastuzumab clinical benefit in advanced esophagogastric cancer.Future Oncol. 2021 Nov;17(31):4101-4114. doi: 10.2217/fon-2021-0203. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Future Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34463133
-
Primary carcinoma of renal calyx.Pathol Res Pract. 2013 Oct;209(10):654-61. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2013.07.007. Epub 2013 Aug 12. Pathol Res Pract. 2013. PMID: 23999038
-
Ado-trastuzumab emtansine in the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma with ERBB2 mutation: a case report and literature review.Anticancer Drugs. 2022 Sep 1;33(8):773-777. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001369. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Anticancer Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35946510 Review.
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 expression in urothelial carcinoma of the renal pelvis: correlation with clinicopathologic parameters.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Apr 15;7(5):2544-50. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24966967 Free PMC article.
-
Paraganglioma of the renal pelvis: a case report and review of literature.Tumori. 2017 Nov 15;103(Suppl. 1):e47-e49. doi: 10.5301/tj.5000677. Tumori. 2017. PMID: 28799639 Review.
References
-
- Khoo ACH, Tang WH. Renal Pelvis Urothelial Carcinoma With Bowel Metastases. Clin Nucl Med 2019; 44: 983–984. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000002797. PMID: 31689282. - PubMed
-
- Wajsman Z, Baumgartner G, Merrin C. Transitional cell carcinoma of ileal loop following cystectomy. Urology 1975; 5: 255–256. doi: 10.1016/0090-4295(75)90025-4. PMID: 1114569. - PubMed
-
- Rouprêt M, Babjuk M, Burger M, et al.. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: 2020 Update. Eur Urol 2021; 79: 62–79. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.05.042. Epub 2020 Jun 24. PMID: 32593530. - PubMed
-
- Soria F, Shariat SF, Lerner SP, et al.. Epidemiology, diagnosis, preoperative evaluation and prognostic assessment of upper-tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC). World J Urol 2017; 35: 379–387. doi: 10.1007/s00345-016-1928-x. Epub 2016 Sep 7. PMID: 27604375. - PubMed
-
- Lohrisch C, Piccart M. An overview of HER2. Semin Oncol 2001; 28: 3–11. PMID: 11774200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous