Emerging small molecule inhibitors of Bach1 as therapeutic agents: Rationale, recent advances, and future perspectives
- PMID: 37919861
- PMCID: PMC11260292
- DOI: 10.1002/bies.202300176
Emerging small molecule inhibitors of Bach1 as therapeutic agents: Rationale, recent advances, and future perspectives
Abstract
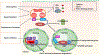
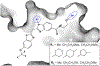
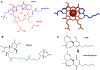
The transcription factor Nrf2 is the master regulator of cellular stress response, facilitating the expression of cytoprotective genes, including those responsible for drug detoxification, immunomodulation, and iron metabolism. FDA-approved Nrf2 activators, Tecfidera and Skyclarys for patients with multiple sclerosis and Friedreich's ataxia, respectively, are non-specific alkylating agents exerting side effects. Nrf2 is under feedback regulation through its target gene, transcriptional repressor Bach1. Specifically, in Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases with Bach1 dysregulation, excessive Bach1 accumulation interferes with Nrf2 activation. Bach1 is a heme sensor protein, which, upon heme binding, is targeted for proteasomal degradation, relieving the repression of Nrf2 target genes. Ideally, a combination of Nrf2 stabilization and Bach1 inhibition is necessary to achieve the full therapeutic benefits of Nrf2 activation. Here, we discuss recent advances and future perspectives in developing small molecule inhibitors of Bach1, highlighting the significance of the Bach1/Nrf2 signaling pathway as a promising neurotherapeutic strategy.
Keywords: Nrf2; bach1; ferroptosis; neurodegeneration; neurotherapeutics.
© 2023 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
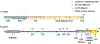
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

