DNA recognition and induced genome modification by a hydroxymethyl-γ tail-clamp peptide nucleic acid
- PMID: 37920723
- PMCID: PMC10621889
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrp.2023.101635
DNA recognition and induced genome modification by a hydroxymethyl-γ tail-clamp peptide nucleic acid
Abstract
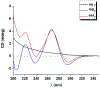
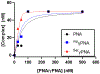
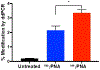
Peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) can target and stimulate recombination reactions in genomic DNA. We have reported that γPNA oligomers possessing the diethylene glycol γ-substituent show improved efficacy over unmodified PNAs in stimulating recombination-induced gene modification. However, this structural modification poses a challenge because of the inherent racemization risk in O-alkylation of the precursory serine side chain. To circumvent this risk and improve γPNA accessibility, we explore the utility of γPNA oligomers possessing the hydroxymethyl-γ moiety for gene-editing applications. We demonstrate that a γPNA oligomer possessing the hydroxymethyl modification, despite weaker preorganization, retains the ability to form a hybrid with the double-stranded DNA target of comparable stability and with higher affinity than that of the diethylene glycol-γPNA. When formulated into poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles, the hydroxymethyl-γPNA stimulates higher frequencies (≥ 1.5-fold) of gene modification than the diethylene glycol γPNA in mouse bone marrow cells.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS P.M.G. is a consultant to and has equity in Gennao Bio, Cybrexa Therapeutics, and pHLIP, Inc., none of which are related to the work reported here. P.M.G., W.M.S., E.Q., and R.B. are inventors on patents assigned to Yale University related to gene editing by PNAs.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Head on Comparison of Self- and Nano-assemblies of Gamma Peptide Nucleic Acid Amphiphiles.Adv Funct Mater. 2022 Feb 9;32(7):2109552. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202109552. Epub 2021 Nov 5. Adv Funct Mater. 2022. PMID: 35210986 Free PMC article.
-
Chimeric γPNA-Invader probes: using intercalator-functionalized oligonucleotides to enhance the DNA-targeting properties of γPNA.Org Biomol Chem. 2020 Feb 21;18(7):1359-1368. doi: 10.1039/c9ob02726b. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Org Biomol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31984413
-
Crystal structure of chiral gammaPNA with complementary DNA strand: insights into the stability and specificity of recognition and conformational preorganization.J Am Chem Soc. 2010 Aug 11;132(31):10717-27. doi: 10.1021/ja907225d. J Am Chem Soc. 2010. PMID: 20681704 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Nanoparticle-based Delivery of Next Generation Peptide Nucleic Acids.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(43):5164-5174. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190117164901. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 30657037 Review.
-
Peptide Nucleic Acids and Gene Editing: Perspectives on Structure and Repair.Molecules. 2020 Feb 8;25(3):735. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030735. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32046275 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-gene oligonucleotide clamps invade dsDNA and downregulate huntingtin expression.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Oct 24;35(4):102348. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102348. eCollection 2024 Dec 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 39763502 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic in utero gene editing as a treatment for cystic fibrosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jun 17;122(24):e2418731122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2418731122. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40493185
-
Harnessing Peptide Nucleic Acids and the Eukaryotic Resolvase MOC1 for Programmable, Precise Generation of Double-Strand DNA Breaks.Anal Chem. 2024 Feb 13;96(6):2599-2609. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c05133. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 38300270 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Cutting-Edge Technologies for the Delivery of Peptide Nucleic Acid.Chemistry. 2025 Jun 17;31(34):e202500469. doi: 10.1002/chem.202500469. Epub 2025 May 21. Chemistry. 2025. PMID: 40351137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of charges on the hybridization kinetics and thermal stability of PNA duplexes.Org Biomol Chem. 2024 Jul 17;22(28):5759-5767. doi: 10.1039/d4ob00887a. Org Biomol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38920402 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McNeer NA, Schleifman EB, Cuthbert A, Brehm M, Jackson A, Cheng C, Anandalingam K, Kumar P, Shultz LD, Greiner DL, et al. (2013). Systemic delivery of triplex-forming PNA and donor DNA by nanoparticles mediates site-specific genome editing of human hematopoietic cells in vivo. Gene Ther. 20, 658–669. 10.1038/gt.2012.82. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schleifman EB, McNeer NA, Jackson A, Yamtich J, Brehm MA, Shultz LD, Greiner DL, Kumar P, Saltzman WM, and Glazer PM (2013). Site-specific Genome Editing in PBMCs With PLGA Nanoparticle-delivered PNAs Confers HIV-1 Resistance in Humanized Mice. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2, e135. 10.1038/mtna.2013.59. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fields RJ, Quijano E, McNeer NA, Caputo C, Bahal R, Anandalingam K, Egan ME, Glazer PM, and Saltzman WM (2015). Modified Poly(lactic-co-glycolic Acid) Nanoparticles for Enhanced Cellular Uptake and Gene Editing in the Lung. Adv. Healthcare Mater 4, 361–366. 10.1002/adhm.201400355. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schleifman EB, Bindra R, Leif J, del Campo J, Rogers FA, Uchil P, Kutsch O, Shultz LD, Kumar P, Greiner DL, and Glazer PM (2011). Targeted Disruption of the CCR5 Gene in Human Hematopoietic Stem Cells Stimulated by Peptide Nucleic Acids. Chem. Biol 18, 1189–1198. 10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.07.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
