Combined Vorinostat and Chloroquine Inhibit Sodium-Iodide Symporter Endocytosis and Enhance Radionuclide Uptake In Vivo
- PMID: 37921808
- PMCID: PMC7615786
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-2043
Combined Vorinostat and Chloroquine Inhibit Sodium-Iodide Symporter Endocytosis and Enhance Radionuclide Uptake In Vivo
Abstract
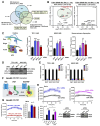
Purpose: Patients with aggressive thyroid cancer are frequently failed by the central therapy of ablative radioiodide (RAI) uptake, due to reduced plasma membrane (PM) localization of the sodium/iodide symporter (NIS). We aimed to understand how NIS is endocytosed away from the PM of human thyroid cancer cells, and whether this was druggable in vivo.
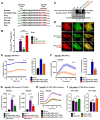
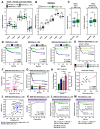
Experimental design: Informed by analysis of endocytic gene expression in patients with aggressive thyroid cancer, we used mutagenesis, NanoBiT interaction assays, cell surface biotinylation assays, RAI uptake, and NanoBRET to understand the mechanisms of NIS endocytosis in transformed cell lines and patient-derived human primary thyroid cells. Systemic drug responses were monitored via 99mTc pertechnetate gamma counting and gene expression in BALB/c mice.
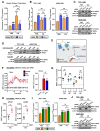
Results: We identified an acidic dipeptide within the NIS C-terminus that mediates binding to the σ2 subunit of the Adaptor Protein 2 (AP2) heterotetramer. We discovered that the FDA-approved drug chloroquine (CQ) modulates NIS accumulation at the PM in a functional manner that is AP2 dependent. In vivo, CQ treatment of BALB/c mice significantly enhanced thyroidal uptake of 99mTc pertechnetate in combination with the histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor vorinostat/SAHA, accompanied by increased thyroidal NIS mRNA. Bioinformatic analyses validated the clinical relevance of AP2 genes with disease-free survival in RAI-treated DTC, enabling construction of an AP2 gene-related risk score classifier for predicting recurrence.
Conclusions: NIS internalization is specifically druggable in vivo. Our data, therefore, provide new translatable potential for improving RAI therapy using FDA-approved drugs in patients with aggressive thyroid cancer. See related commentary by Lechner and Brent, p. 1220.
©2023 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors assert they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
A New Twist on a Classic: Enhancing Radioiodine Uptake in Advanced Thyroid Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Apr 1;30(7):1220-1222. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-3503. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38197869 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Targeting Src tyrosine kinase to enhance radioiodide uptake in breast cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2025 Aug 20;32(8):e240312. doi: 10.1530/ERC-24-0312. Print 2025 Aug 1. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40748136
-
Lomibuvir sensitizes radioiodine-resistant thyroid cancer cell lines to radioiodine treatment by targeting hTERT RNA-dependent polymerase activity.J Endocrinol Invest. 2025 Aug;48(8):1797-1810. doi: 10.1007/s40618-025-02598-1. Epub 2025 May 13. J Endocrinol Invest. 2025. PMID: 40358852
-
Vorinostat, a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, promotes cell cycle arrest and re-sensitizes rituximab- and chemo-resistant lymphoma cells to chemotherapy agents.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016 Feb;142(2):379-87. doi: 10.1007/s00432-015-2026-y. Epub 2015 Aug 28. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26314218 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuraminidase inhibitors for preventing and treating influenza in healthy adults and children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1:CD008965. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008965.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 10;(4):CD008965. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008965.pub4. PMID: 22258996 Updated.
Cited by
-
Functional characterization of novel compound heterozygous missense SLC5A5 gene variants causing congenital dyshormonogenic hypothyroidism.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Dec 19;15:1465176. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1465176. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39749016 Free PMC article.
-
Novel molecular typing reveals the risk of recurrence in patients with early-stage papillary thyroid cancer.Thyroid Res. 2024 Apr 1;17(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13044-024-00193-9. Thyroid Res. 2024. PMID: 38556856 Free PMC article.
-
A New Twist on a Classic: Enhancing Radioiodine Uptake in Advanced Thyroid Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Apr 1;30(7):1220-1222. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-3503. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38197869 Free PMC article.
-
A calcium-sensing receptor dileucine motif directs internalization to spatially distinct endosomal signaling pathways.iScience. 2025 May 13;28(6):112651. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112651. eCollection 2025 Jun 20. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40510119 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Durante C, Puxeddu E, Ferretti E, Morisi R, Moretti S, Bruno R, et al. BRAF mutations in papillary thyroid carcinomas inhibit genes involved in iodine metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92(7):2840–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

