[Contemporary diagnosis and management of congenital microtia and aural atresia : Part 1: Principles and diagnosis]
- PMID: 37921885
- PMCID: PMC10663219
- DOI: 10.1007/s00106-023-01381-z
[Contemporary diagnosis and management of congenital microtia and aural atresia : Part 1: Principles and diagnosis]
Abstract
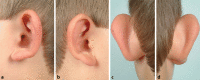
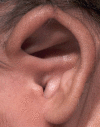
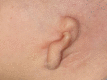
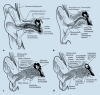
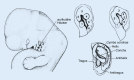
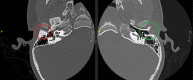
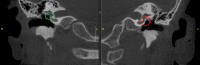
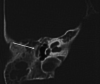
Congenital malformations of the pinna and aural atresia can result in major aesthetic and functional deficits. Knowledge about embryologic developments and established classification systems is an essential requirement when dealing with affected patients. Early detection of deficiencies and introduction of appropriate diagnostic measures is vital to initiate adequate therapies and prevent long-term disabilities. Treatment for malformations of the pinna-if requested-is mostly surgical, infrequently an epithesis is applied. As in other surgical fields, tissue engineering will likely play a crucial role in the future. Treatment of aural stenosis and atresia aims at improvement of hearing levels and prevention of secondary complications like cholesteatoma and chronic otorrhea. Auditory rehabilitation comprises a spectrum from conventional hearing aids to invasive hearing implants, the latter being favored in recent years.
Angeborene Fehlbildungen der Ohrmuschel und des äußeren Gehörgangs können mit schweren ästhetischen und funktionellen Defiziten einhergehen. Neben dem Verständnis embryologischer Grundlagen ist auch die Klassifikation derartiger Anomalien für die Behandlung essenziell. Die frühzeitige Erkennung einer Fehlbildung sowie die Einleitung zeitgerechter Diagnostik sind essenziell, um durch eine adäquate Therapie langfristige Einschränkungen zu verhindern. Ohrmuscheldysplasien werden heute meist operativ, seltener mittels Epithese korrigiert. Die Methoden des „tissue engineering“ sind seit Langem in der Erprobung und könnten in Zukunft eine wesentliche Rolle spielen. Die Behandlung von Gehörgangsstenosen und -atresien bezweckt neben einer Hörverbesserung auch die Verhinderung von Folgeerkrankungen. Darunter finden sich u. a. Cholesteatome oder rezidivierende Infekte. Die Hörrehabilitation umfasst konventionelle und implantierbare Hörgeräte, wobei der Trend zu Letzteren tendiert.
Keywords: Cholesteatoma; Congenital abnormalities; Evoked response audiometry; Implantable hearing aids; Rehabilitation.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Similar articles
-
[Contemporary diagnosis and management of congenital microtia and aural atresia : Part 2: Overview of therapeutic approaches].HNO. 2024 Jan;72(1):57-68. doi: 10.1007/s00106-023-01386-8. Epub 2023 Dec 4. HNO. 2024. PMID: 38047932 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
Surgery or implantable hearing devices in children with congenital aural atresia: 25 years of our experience.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015 Jul;79(7):975-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2015.03.031. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015. PMID: 25930173
-
International Consensus Recommendations on Microtia, Aural Atresia and Functional Ear Reconstruction.J Int Adv Otol. 2019 Aug;15(2):204-208. doi: 10.5152/iao.2019.7383. J Int Adv Otol. 2019. PMID: 31418720 Free PMC article.
-
The Lübeck flowchart for functional and aesthetic rehabilitation of aural atresia and microtia.Otol Neurotol. 2012 Oct;33(8):1363-7. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e3182659adf. Otol Neurotol. 2012. PMID: 22918112
-
Management of hearing loss and the normal ear in cases of unilateral Microtia with aural atresia.Laryngoscope. 2016 Jun;126(6):1470-4. doi: 10.1002/lary.25530. Epub 2015 Aug 8. Laryngoscope. 2016. PMID: 26256547
References
-
- Jafek BW, Nager GT, Strife J, et al. Congenital aural atresia: an analysis of 311 cases. Trans Sect Otolaryngol Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1975;80:588–595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials