Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen-Targeting Alpha Emitter via Antibody Delivery for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of 225Ac-J591
- PMID: 37922438
- PMCID: PMC10906595
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.00573
Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen-Targeting Alpha Emitter via Antibody Delivery for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of 225Ac-J591
Abstract
Purpose: Novel therapies are needed to extend survival in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA), a cell surface antigen overexpressed in PC, provides a validated target. This dose-escalation study investigated the safety, efficacy, maximum tolerated dose (MTD), and recommended phase II dose (RP2D) for 225Ac-J591, anti-PSMA monoclonal antibody J591 radiolabeled with the alpha emitter actinium-225.
Methods: Following investigational new drug-enabling preclinical studies, we enrolled patients with progressive mCRPC that was refractory to or who refused standard treatment options (including androgen receptor pathway inhibitor and had received or been deemed ineligible for taxane chemotherapy). No selection for PSMA was performed. Patients received a single dose of 225Ac-J591 at one of seven dose-escalation levels followed by expansion at the highest dose. Primary end point of dose-escalation cohort was determination of dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) and RP2D.
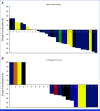
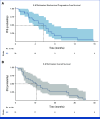
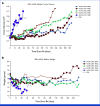
Results: Radiochemistry and animal studies were favorable. Thirty-two patients received 225Ac-J591 in an accelerated dose-escalation design (22 in dose escalation, 10 in expansion). One patient (1 of 22; 4.5%) experienced DLT in cohort 6 (80 KBq/kg) but none in cohort 7; MTD was not reached, and RP2D was the highest dose level (93.3 KBq/kg). The majority of high-grade adverse events (AEs) were hematologic with an apparent relationship with administered radioactivity. Nonhematologic AEs were generally of low grade. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) declines and circulating tumor cell (CTC) control were observed: 46.9% had at least 50% PSA decline at any time (34.4% confirmed PSA response), and protocol-defined CTC count response occurred in 13 of 22 (59.1%).
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the first-in-human phase I dose-escalation trial of a single dose of 225Ac-J591 in 32 patients with pretreated progressive mCRPC demonstrated safety and preliminary efficacy signals. Further investigation is underway.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03276572.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, et al. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:17–48. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Bostwick DG, Pacelli A, Blute M, et al. Prostate specific membrane antigen expression in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and adenocarcinoma: A study of 184 cases. Cancer. 1998;82:2256–2261. - PubMed
-
- Silver DA, Pellicer I, Fair WR, et al. Prostate-specific membrane antigen expression in normal and malignant human tissues. Clin Cancer Res. 1997;3:81–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

