Molecular mechanisms of AMPK/YAP/NLRP3 signaling pathway affecting the occurrence and development of ankylosing spondylitis
- PMID: 37925428
- PMCID: PMC10625209
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-023-04200-x
Molecular mechanisms of AMPK/YAP/NLRP3 signaling pathway affecting the occurrence and development of ankylosing spondylitis
Abstract
Background: Investigate the AMPK (protein kinase AMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha 1)/YAP (Yes1 associated transcriptional regulator)/NLRP3 (NLR family pyrin domain containing 3) signaling pathway's role in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) development using public database analysis, in vitro and in vivo experiments.
Methods: Retrieve AS dataset, analyze differential gene expression in R, conduct functional enrichment analysis, collect 30 AS patient and 30 normal control samples, and construct a mouse model. ELISA, IP, and knockdown experiments were performed to detect expression changes.
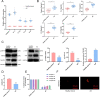
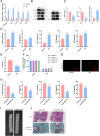
Results: NLRP3 was identified as a significant AS-related gene. Caspase-1, IL-1β, IL-17A, IL-18, IL-23, YAP, and NLRP3 were upregulated in AS patients. Overexpressing AMPK inhibited YAP's blockade on NLRP3 ubiquitination, reducing ossification in fibroblasts. Inhibiting AMPK exacerbated AS symptoms in AS mice.
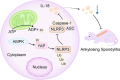
Conclusion: AMPK may suppress YAP expression, leading to NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition and AS alleviation.
Keywords: AMPK; Ankylosing spondylitis; NLRP3; Phosphorylation activation; Ubiquitination degradation; YAP.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Song IH, Hermann K, Haibel H, Althoff CE, Listing J, Burmester G, et al. Effects of etanercept versus sulfasalazine in early axial spondyloarthritis on active inflammatory lesions as detected by whole-body MRI (ESTHER): a 48-week randomised controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:590–596. doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.139667. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

