Bioinspired soft robots for deep-sea exploration
- PMID: 37925504
- PMCID: PMC10625581
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42882-3
Bioinspired soft robots for deep-sea exploration
Abstract
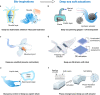
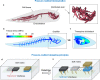
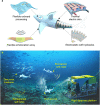
The deep ocean, Earth's untouched expanse, presents immense challenges for exploration due to its extreme pressure, temperature, and darkness. Unlike traditional marine robots that require specialized metallic vessels for protection, deep-sea species thrive without such cumbersome pressure-resistant designs. Their pressure-adaptive forms, unique propulsion methods, and advanced senses have inspired innovation in designing lightweight, compact soft machines. This perspective addresses challenges, recent strides, and design strategies for bioinspired deep-sea soft robots. Drawing from abyssal life, it explores the actuation, sensing, power, and pressure resilience of multifunctional deep-sea soft robots, offering game-changing solutions for profound exploration and operation in harsh conditions.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 12102398/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 51925904/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 52088102/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 11822207/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 91748209/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

