Vagus nerve stimulation for treating developmental and epileptic encephalopathy in young children
- PMID: 37928141
- PMCID: PMC10624125
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1191831
Vagus nerve stimulation for treating developmental and epileptic encephalopathy in young children
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the clinical variables that might predict the outcome of developmental and epileptic encephalopathy (DEE) after vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) therapy and identify the risk factors for poor long-term outcome.
Patients and methods: We retrospectively studied 32 consecutive children with drug-resistant DEE who had undergone VNS surgery from April 2019 to July 2021, which were not suitable for corpus callosotomy. In spite of combining valproic acid, levetiracetam, lamotrigine, topiramate, etc. (standard anti-seizure medicine available in China) it has not been possible to effectively reduce seizures in the population we investigate (Cannabidiol and brivaracetam were not available in China). A responder was defined as a frequency reduction decrease > 50%. Seizure freedom was defined as freedom from seizures for at least 6 months. Sex, electroencephalograph (EEG) group, neurodevelopment, time lag, gene mutation, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and epilepsy syndrome were analyzed with Fisher's exact test, The age at onset and age at VNS therapy were analyzed with Kruskal-Wallis test, statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05. And used the effect size to correction.
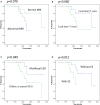
Results: Among the 32 patients, the median age at VNS implantation was 4.7 years (range: 1-12 years). At the most recent follow-up, five children (15.6%) were seizure-free and 22 (68.8%) were responders. Univariate analysis demonstrated that the responders were significantly associated with mild development delay/intellectual disability (p = 0.044; phi coefficient = 0.357) and a multifocal EEG pattern (p = 0.022; phi coefficient = -0.405). Kaplan-Meier survival analyses demonstrated that a multifocal EEG pattern (p = 0.049) and DEE without epileptic spasm (ES) (p = 0.012) were statistically significant (p = 0.030). Multivariate analysis demonstrated that DEE with ES had significant predictive value for poor long-term outcome (p = 0.014, hazard ratio = 5.433, confidence interval = 1.402-21.058).
Conclusions: Our study suggested that VNS was a generally effective adjunct treatment for DEE. Although the predictive factors for VNS efficacy remain unclear, it should be emphasized that patients with ES are not suitable candidates for epilepsy surgery. Further investigations are needed to validate the present results.
Keywords: cognitive disorder; developmental and epileptic encephalopathy; drug-resistant epilepsy; gene mutation; vagus nerve stimulation.
Copyright © 2023 Geng, Hu, Meng, Zhang, Zhang, Chen, Zhang, Gao, Liu and Shi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term outcome of vagus nerve stimulation therapy in drug-resistant epilepsy: a retrospective single-center study.Front Neurol. 2025 May 9;16:1564735. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1564735. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40417112 Free PMC article.
-
Norwegian population-based study of effectiveness of vagus nerve stimulation in patients with developmental and epileptic encephalopathies.Epilepsia Open. 2024 Apr;9(2):704-716. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12908. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Epilepsia Open. 2024. PMID: 38318727 Free PMC article.
-
Early vagus nerve stimulator implantation as a main predictor of positive outcome in pediatric patients with epileptic encephalopathy.Epileptic Disord. 2021 Aug 1;23(4):563-571. doi: 10.1684/epd.2021.1299. Epileptic Disord. 2021. PMID: 34184987
-
Electrical stimulation for drug-resistant epilepsy: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2013 Oct 1;13(18):1-37. eCollection 2013. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2013. PMID: 24228081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Palliative epilepsy surgery in Dravet syndrome-case series and review of the literature.Childs Nerv Syst. 2016 Sep;32(9):1703-8. doi: 10.1007/s00381-016-3201-4. Epub 2016 Jul 27. Childs Nerv Syst. 2016. PMID: 27465677 Review.
Cited by
-
Expanding the therapeutic role of highly purified cannabidiol in monogenic epilepsies: A multicenter real-world study.Epilepsia. 2025 Jul;66(7):2253-2267. doi: 10.1111/epi.18378. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Epilepsia. 2025. PMID: 40126049 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcome of vagus nerve stimulation therapy in drug-resistant epilepsy: a retrospective single-center study.Front Neurol. 2025 May 9;16:1564735. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1564735. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40417112 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

