Genetic architecture of ear traits based on association mapping and co-expression networks in maize inbred lines and hybrids
- PMID: 37928364
- PMCID: PMC10624778
- DOI: 10.1007/s11032-023-01426-9
Genetic architecture of ear traits based on association mapping and co-expression networks in maize inbred lines and hybrids
Abstract
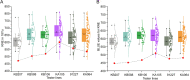
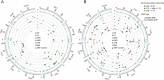
Ear traits are key contributors to grain yield in maize; therefore, exploring their genetic basis facilitates the improvement of grain yield. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms of ear traits remain obscure in both inbred lines and hybrids. Here, two association panels, respectively, comprising 203 inbred lines (IP) and 246 F1 hybrids (HP) were employed to identify candidate genes for six ear traits. The IP showed higher phenotypic variation and lower phenotypic mean than the HP for all traits, except ear tip-barrenness length. By conducting a genome-wide association study (GWAS) across multiple environments, 101 and 228 significant single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with six ear traits were identified in the IP and HP, respectively. Of these significant SNPs identified in the HP, most showed complete-incomplete dominance and over-dominance effects for each ear trait. Combining a gene co-expression network with GWAS results, 186 and 440 candidate genes were predicted in the IP and HP, respectively, including known ear development genes ids1 and sid1. Of these, nine candidate genes were detected in both populations and expressed in maize ear and spikelet tissues. Furthermore, two key shared genes (GRMZM2G143330 and GRMZM2G171139) in both populations were found to be significantly associated with ear traits in the maize Goodman diversity panel with high-density variations. These findings advance our knowledge of the genetic architecture of ear traits between inbred lines and hybrids and provide a valuable resource for the genetic improvement of ear traits in maize.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s11032-023-01426-9.
Keywords: Association mapping; Co-expression network; Ear traits; Hybrid; Inbred line; Maize.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V. 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Analysis of the genetic architecture of maize ear and grain morphological traits by combined linkage and association mapping.Theor Appl Genet. 2017 May;130(5):1011-1029. doi: 10.1007/s00122-017-2867-7. Epub 2017 Feb 18. Theor Appl Genet. 2017. PMID: 28215025
-
A combination of linkage mapping and GWAS brings new elements on the genetic basis of yield-related traits in maize across multiple environments.Theor Appl Genet. 2020 Oct;133(10):2881-2895. doi: 10.1007/s00122-020-03639-4. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Theor Appl Genet. 2020. PMID: 32594266
-
GWAS and Meta-QTL Analysis of Yield-Related Ear Traits in Maize.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 8;12(22):3806. doi: 10.3390/plants12223806. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38005703 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Diversity and Genome-Wide Association Study of Major Ear Quantitative Traits Using High-Density SNPs in Maize.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Jul 9;9:966. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00966. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30038634 Free PMC article.
-
Hotspot Regions of Quantitative Trait Loci and Candidate Genes for Ear-Related Traits in Maize: A Literature Review.Genes (Basel). 2023 Dec 21;15(1):15. doi: 10.3390/genes15010015. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38275597 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide association study for plant height and ear height in maize under well-watered and water-stressed conditions.BMC Genomics. 2025 Aug 12;26(1):745. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11932-z. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40797183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bates DM. lme4: mixed-effects modeling with R. 2010.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

