Association between psoriasis and serum apolipoprotein A1 and B: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37928384
- PMCID: PMC10622706
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21168
Association between psoriasis and serum apolipoprotein A1 and B: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Psoriasis has been linked to dyslipidemia. However, the magnitude of the association between psoriasis and serum apolipoproteins A1 and B remains unclear.
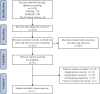
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases for eligible studies published before August 10, 2023. Data were pooled using Stata software. We adopted a random-effects model for the meta-analysis. Additionally, we conducted subgroup analyses of the studies according to the psoriasis type and matched body mass index (BMI).
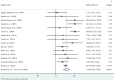
Results: Seventeen studies involving 2467 participants were included. Psoriasis was associated with decreased serum apolipoprotein A1 (weighted mean difference [WMD] = -9.05, P < 0.001) and increased serum apolipoprotein B (WMD = 11.68, P < 0.001). In subgroup analysis after matching BMI, the findings showing an association of psoriasis with serum apolipoprotein A1 (WMD = -14.07, P < 0.001) and serum apolipoprotein B (WMD = 13.07, P < 0.001) were consistent with the overall results. The subgroup analysis for the presence or absence of psoriatic arthritis showed that serum apolipoprotein A1 was significantly decreased in psoriasis with (WMD = -11.29, P < 0.001) and without arthritis (WMD = -8.69, P = 0.039); whereas serum apolipoprotein B was significantly increased in psoriasis with (WMD = 13.57, P < 0.001) and without arthritis (WMD = 9.21, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Our study revealed that psoriasis is associated with decreased serum apolipoprotein A1 and increased serum apolipoprotein B levels compared with healthy controls.
Keywords: Apolipoprotein A1; Apolipoprotein B; Lipid metabolism; Meta-analysis; Psoriasis.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Association Between Psoriasis and Subclinical Atherosclerosis: A Meta-Analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 May;95(20):e3576. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003576. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27196459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The association of the apolipoprotein B/A1 ratio and the metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023 Jun 17;23(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s40200-023-01235-z. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023. PMID: 38932877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum levels of YKL-40 are increased in patients with psoriasis: a meta-analysis.Postgrad Med. 2019 Aug;131(6):405-412. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2019.1643634. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Postgrad Med. 2019. PMID: 31298974
-
Association between Homocysteine Levels and Psoriasis: A Meta-Analysis.Ann Dermatol. 2019 Aug;31(4):378-386. doi: 10.5021/ad.2019.31.4.378. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Ann Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 33911615 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of serum lipid, lipoprotein, and apolipoprotein levels in psoriatic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies.Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2019 Dec;36(6):692-702. doi: 10.5114/ada.2019.91420. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2019. PMID: 31997997 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Apolipoproteins in Psoriasis: The Effect of Acitretin Treatment and UVB Phototherapy.Metabolites. 2025 Mar 12;15(3):196. doi: 10.3390/metabo15030196. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 40137160 Free PMC article.
-
New Perspectives on Nutraceutical Insulin Sensitizing Agents in the Treatment of Psoriasis and Other Dermatological Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 4;26(15):7538. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157538. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors on lipid profiles in patients with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 4;15:1354593. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1354593. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38500874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moini J.A., Ayati M.H., Nadiri A.A., Nasimi D.A.R. Efficacy of hydrotherapy, spa therapy, and balneotherapy for psoriasis and atopic dermatitis: a systematic review. Int. J. Dermatol. 2022 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

