Possible Rates of Detection of Neonatal Sepsis Pathogens in the Context of Microbiological Diagnostics in Mothers - Real World Data
- PMID: 37928410
- PMCID: PMC10624541
- DOI: 10.1055/a-2091-0856
Possible Rates of Detection of Neonatal Sepsis Pathogens in the Context of Microbiological Diagnostics in Mothers - Real World Data
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to identify the rate of detection of neonatal sepsis pathogens in maternal microbiological smears.
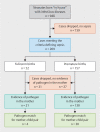
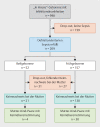
Study design: This is a retrospective study conducted at a Level 1 perinatal center in the context of routine care from 2014 to 2019. For all premature infants and neonates with neonatal sepsis, the neonatal and maternal microbiological findings were examined to see if there was a match.
Results: During the study period, a total of 948 premature or newborn infants were identified as having a neonatal infection. Among all of the premature or newborn infants, 209 (22%) met the diagnostic criteria for neonatal sepsis; of these, 157 were premature births and 52 were full-term births. We evaluated the microbiological findings for these 209 mother and child pairs. No pathogens were detected in 27 out of 157 mothers of premature infants (17.1%) and in 31 out of 52 mothers of full-term infants (59.6%). In the premature infant group there were pairs with matching pathogens in 30 out of 130 cases (23.1%, 95% CI: 16.1-31.3), and in the full-term infant group there was a match in 4 out of 21 cases (19%, 95% CI: 5.4-41.9). The number needed to test to have a 90% probability of success for pathogen detection varies between 9 and 11 in the most favorable case and 26 and 32 in the least favorable case, depending on the evaluation method.
Conclusion: In cases of neonatal sepsis, the sepsis-causing pathogen was successfully detected through prior analysis of a maternal smear in 7% of full-term infants and in 19% of premature infants. The number needed to test was relatively high in all groups. The value of maternal smears for identifying neonatal sepsis-causing pathogens needs to be critically questioned.
Keywords: bacterial infection; infections; normal birth; pregnancy; premature birth.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial-License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maternal sepsis incidence, aetiology and outcome for mother and fetus: a prospective study.BJOG. 2015 Apr;122(5):663-71. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.12892. Epub 2014 May 23. BJOG. 2015. PMID: 24862293 Review.
-
Perinatal Antibiotic Exposure Affects the Transmission between Maternal and Neonatal Microbiota and Is Associated with Early-Onset Sepsis.mSphere. 2020 Feb 19;5(1):e00984-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00984-19. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32075882 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal bacterial colonization and neonatal early-onset sepsis: A case-control study.J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2022;15(4):813-819. doi: 10.3233/NPM-210978. J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2022. PMID: 35811543
-
Bacterial vaginosis and adverse outcomes among full-term infants: a cohort study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016 Sep 22;16(1):278. doi: 10.1186/s12884-016-1073-y. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016. PMID: 27658456 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal probiotic supplementation for prevention of morbidity and mortality in preterm infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Dec 12;12(12):CD012519. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012519.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30548483 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous