Clonal Relationship and Mutation Analysis in Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma/Waldenström Macroglobulinemia Associated With Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
- PMID: 37928625
- PMCID: PMC10621888
- DOI: 10.1097/HS9.0000000000000976
Clonal Relationship and Mutation Analysis in Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma/Waldenström Macroglobulinemia Associated With Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
Abstract
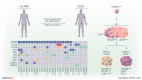
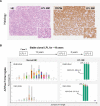
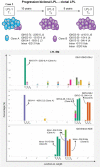
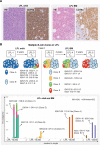
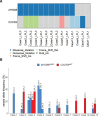
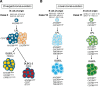
Patients with lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström macroglobulinemia (LPL/WM) occasionally develop diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). This mostly results from LPL/WM transformation, although clonally unrelated DLBCL can also arise. LPL/WM is characterized by activating MYD88L265P (>95%) and CXCR4 mutations (~30%), but the genetic drivers of transformation remain to be identified. Here, in thirteen LPL/WM patients who developed DLBCL, the clonal relationship of LPL and DLBCL together with mutations contributing to transformation were investigated. In 2 LPL/WM patients (15%), high-throughput sequencing of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements showed evidence of >1 clonal B-cell population in LPL tissue biopsies. In the majority of LPL/WM patients, DLBCL presentations were clonally related to the dominant clone in LPL, providing evidence of transformation. However, in 3 patients (23%), DLBCL was clonally unrelated to the major malignant B-cell clone in LPL, of which 2 patients developed de novo DLBCL. In this study cohort, LPL displayed MYD88L265P mutation in 8 out of eleven patients analyzed (73%), while CXCR4 mutations were observed in 6 cases (55%). MYD88WT LPL biopsies present in 3 patients (27%) were characterized by CD79B and TNFAIP3 mutations. Upon transformation, DLBCL acquired novel mutations targeting BTG1, BTG2, CD79B, CARD11, TP53, and PIM1. Together, we demonstrate variable clonal B-cell dynamics in LPL/WM patients developing DLBCL, and the occurrence of clonally unrelated DLBCL in about one-quarter of LPL/WM patients. Moreover, we identified commonly mutated genes upon DLBCL transformation, which together with preserved mutations already present in LPL characterize the mutational landscape of DLBCL occurrences in LPL/WM patients.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the European Hematology Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Vitolo U, Ferreri AJ, Montoto S. Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma-Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2008;67:172–185. - PubMed
-
- Lin P, Mansoor A, Bueso-Ramos C, et al. . Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma occurring in patients with lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia clinicopathologic features of 12 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 2003;120:246–253. - PubMed
-
- Leleu X, Soumerai J, Roccaro A, et al. . Increased incidence of transformation and myelodysplasia/acute leukemia in patients with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia treated with nucleoside analogs. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:250–255. - PubMed
-
- Castillo JJ, Gustine J, Meid K, et al. . Histological transformation to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in patients with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Am J Hematol. 2016;91:1032–1035. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
