High confidence QTLs and key genes identified using Meta-QTL analysis for enhancing heat tolerance in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.)
- PMID: 37929162
- PMCID: PMC10623133
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1274759
High confidence QTLs and key genes identified using Meta-QTL analysis for enhancing heat tolerance in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.)
Abstract
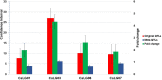
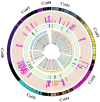
The rising global temperatures seriously threaten sustainable crop production, particularly the productivity and production of heat-sensitive crops like chickpeas. Multiple QTLs have been identified to enhance the heat stress tolerance in chickpeas, but their successful use in breeding programs remains limited. Towards this direction, we constructed a high-density genetic map spanning 2233.5 cM with 1069 markers. Using 138 QTLs reported earlier, we identified six Meta-QTL regions for heat tolerance whose confidence interval was reduced by 2.7-folds compared to the reported QTLs. Meta-QTLs identified on CaLG01 and CaLG06 harbor QTLs for important traits, including days to 50% flowering, days to maturity, days to flower initiation, days to pod initiation, number of filled pods, visual score, seed yield per plant, biological yield per plant, chlorophyll content, and harvest index. In addition, key genes identified in Meta-QTL regions like Pollen receptor-like kinase 3 (CaPRK3), Flowering-promoting factor 1 (CaFPF1), Flowering Locus C (CaFLC), Heat stress transcription factor A-5 (CaHsfsA5), and Pollen-specific leucine-rich repeat extensins (CaLRXs) play an important role in regulating the flowering time, pollen germination, and growth. The consensus genomic regions, and the key genes reported in this study can be used in genomics-assisted breeding for enhancing heat tolerance and developing heat-resilient chickpea cultivars.
Keywords: Meta-QTLs; candidate genes; confidence interval; heat stress; recombinant inbred lines.
Copyright © 2023 Kumar, Sharma, Rangari, Jha, Sahu, Paul, Gupta, Gangurde, Kudapa, Mir, Gaur, Varshney, Elango and Thudi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer RS declared a shared affiliation with the authors PG, HK to the handling editor at the time of review. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- Bheemanahalli R., Vennam R. R., Ramamoorthy P., Reddy K. R. (2022). Effects of post-flowering heat and drought stresses on physiology, yield, and quality in maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Stress. 6, 100106. doi: 10.1016/j.stress.2022.100106 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

