Activation of the integrated stress response rewires cardiac metabolism in Barth syndrome
- PMID: 37930434
- PMCID: PMC10628049
- DOI: 10.1007/s00395-023-01017-x
Activation of the integrated stress response rewires cardiac metabolism in Barth syndrome
Abstract
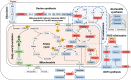
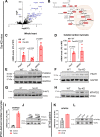
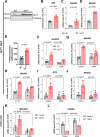
Barth Syndrome (BTHS) is an inherited cardiomyopathy caused by defects in the mitochondrial transacylase TAFAZZIN (Taz), required for the synthesis of the phospholipid cardiolipin. BTHS is characterized by heart failure, increased propensity for arrhythmias and a blunted inotropic reserve. Defects in Ca2+-induced Krebs cycle activation contribute to these functional defects, but despite oxidation of pyridine nucleotides, no oxidative stress developed in the heart. Here, we investigated how retrograde signaling pathways orchestrate metabolic rewiring to compensate for mitochondrial defects. In mice with an inducible knockdown (KD) of TAFAZZIN, and in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiac myocytes, mitochondrial uptake and oxidation of fatty acids was strongly decreased, while glucose uptake was increased. Unbiased transcriptomic analyses revealed that the activation of the eIF2α/ATF4 axis of the integrated stress response upregulates one-carbon metabolism, which diverts glycolytic intermediates towards the biosynthesis of serine and fuels the biosynthesis of glutathione. In addition, strong upregulation of the glutamate/cystine antiporter xCT increases cardiac cystine import required for glutathione synthesis. Increased glutamate uptake facilitates anaplerotic replenishment of the Krebs cycle, sustaining energy production and antioxidative pathways. These data indicate that ATF4-driven rewiring of metabolism compensates for defects in mitochondrial uptake of fatty acids to sustain energy production and antioxidation.
Keywords: Amino acid; Barth syndrome; Fatty acid oxidation; Metabolism; Mitochondria; Oxidative stress.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
CM received speaker and consultancy honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk. TT is founder and shareholder of Cardior Pharmaceuticals (outside of this study). TT filed and licensed patents about the use of noncoding RNAs (outside of the paper).
Figures





References
-
- Ardanaz N, Yang XP, Cifuentes ME, Haurani MJ, Jackson KW, Liao TD, Carretero OA, Pagano PJ. Lack of glutathione peroxidase 1 accelerates cardiac-specific hypertrophy and dysfunction in angiotensin II hypertension. Hypertension. 2010;55:116–123. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.135715. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Badolia R, Ramadurai DKA, Abel ED, Ferrin P, Taleb I, Shankar TS, Krokidi AT, Navankasattusas S, McKellar SH, Yin M, Kfoury AG, Wever-Pinzon O, Fang JC, Selzman CH, Chaudhuri D, Rutter J, Drakos SG. The role of nonglycolytic glucose metabolism in myocardial recovery upon mechanical unloading and circulatory support in chronic heart failure. Circulation. 2020;142:259–274. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.044452. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

